Duration of Treatment
5 to 6 hours
Days of Stay
1 to 5 month
Anesthesia
General Anesthesia
Cost
20000 USD
How Much Does Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India?
Are we looking for Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India at an affordable cost? Here, we answer the question and explain how to choose the top doctors for better results.
We have shortlisted the list of the best top Pancreas Transplant Surgery Hospitals and Surgeons based on Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of surgeons, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India: starting from 20000 to 30000 USD.
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD (as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day)
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day).
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will be planned after the fresh evaluation reports.
- In India, Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India can vary as per the diagnosis, patient's conditions, Bariatric surgeon experience, Implant quality, hospital facilities, and city.
- To make an appointment, learn more about the Gastric, read the information below, or call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782. Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
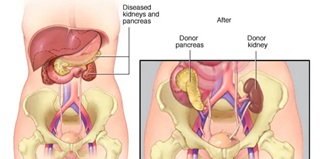
What is Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
A pancreas transplant is a surgical procedure to implant a healthy pancreas from a deceased donor into a person whose pancreas no longer functions properly. The primary purpose of a pancreas transplant is to treat type 1 diabetes, a condition where the pancreas cannot produce insulin. Here are the main points about pancreas transplant surgery:
Indications
- Type 1 Diabetes: Most commonly performed for people with type 1 diabetes who have severe complications, such as hypoglycemia unawareness, or kidney failure.
- Type 2 Diabetes: In rare cases, it can be performed for type 2 diabetes if the patient meets specific criteria.
Types of Pancreas Transplants
- Pancreas Alone: For patients with severe diabetes without kidney disease.
- Pancreas-Kidney Transplant: For patients with both diabetes and kidney failure.
- Pancreas After Kidney Transplant: For patients who have already had a kidney transplant and later receive a pancreas transplant.
Who can have a pancreas transplant?
-
Age: Generally, candidates are between 18 and 65, but this can vary based on individual health status.
- Overall Health: Candidates should be healthy enough to undergo major surgery and handle the immunosuppressive medications required after transplantation.
- Absence of Contraindications: Candidates should not have significant health issues such as active infections, recent cancer, or severe cardiovascular disease.
- Compliance: Candidates must demonstrate the ability to adhere to the rigorous post-transplant care regimen, including taking medications as prescribed and attending regular follow-up appointments.
Evaluation Process
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Comprehensive evaluation to assess the patient's overall health and suitability for surgery.
- Psychosocial Evaluation: Assessment to ensure the patient can handle transplantation's psychological and social demands.
- Laboratory and Imaging Tests: To assess organ function and overall health status.
- Consultations: With specialists such as endocrinologists, nephrologists, and transplant surgeons.
Relative Contraindications
- Obesity: Excessive weight can complicate surgery and recovery.
- Substance Abuse: Active substance abuse is typically a contraindication.
- Non-compliance: History of non-compliance with medical treatments.
What is the Risk Factor of Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
Pancreas transplant surgery carries several risks, which can be categorized into short-term and long-term complications. Here are the primary risk factors:
Short-Term Risks
- Surgical Complications:
- Bleeding: Significant blood loss during or after surgery.
- Infection: Risk of infection at the surgical site or within the abdomen.
- Blood Clots: Formation of clots in the blood vessels of the transplanted pancreas.
- Organ Rejection:
- Acute Rejection: The body's immune system attacks the new pancreas, which can occur within weeks to months after transplantation.
- Chronic Rejection: A slower, ongoing immune response that can lead to gradual loss of pancreas function over time.
- Pancreatitis:
- Inflammation of the transplanted pancreas can cause abdominal pain and digestive issues.
- Graft Thrombosis:
- Blood clots can form in the blood vessels supplying the new pancreas, leading to graft failure.
- Delayed Graft Function:
- The transplanted pancreas may not work immediately, requiring additional medical support.
Long-Term Risks
- Infections:
- Increased risk of infections due to the lifelong need for immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection.
- Immunosuppressive Medication Side Effects:
- Kidney Damage: Some immunosuppressive drugs can harm the kidneys.
- High Blood Pressure: Immunosuppressants can cause hypertension.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels are common.
- Diabetes: Some patients may develop diabetes post-transplant.
- Increased Cancer Risk: Long-term immunosuppression can increase the risk of certain cancers.
- Recurrence of Diabetes:
- While rare, diabetes can recur in the transplanted pancreas.
- Psychosocial Issues:
- The emotional and psychological impact of transplantation, including anxiety, depression, and stress related to the need for ongoing medical care.
Other Considerations
- Organ Availability:
- The scarcity of suitable donor organs can lead to long waiting times, during which the patient's condition may deteriorate.
- Quality of Life:
- While many patients experience significant improvements, the need for continuous medical follow-up and potential complications can impact quality of life.
- Financial Costs:
- Surgery, hospitalization, medications, and long-term follow-up care costs can be substantial.
Mitigating Risks
- Thorough Evaluation: Comprehensive pre-transplant evaluation to ensure candidates are suitable.
- Experienced Surgical Team: Having surgery performed by a skilled and experienced transplant team.
- Post-Operative Care: Close monitoring and adherence to medical recommendations post-surgery.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support overall health and the function of the transplanted organ.
Patients considering a pancreas transplant should discuss these risks and benefits in detail with their transplant team to make an informed decision.
What is the preparation needed before Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
Preparing for a pancreas transplant surgery involves several steps to ensure that the patient is in optimal health and ready for the procedure. Here are the key aspects of the preparation process:
Medical Evaluation
- Comprehensive Medical History and Physical Examination:
- A detailed review of the patient's medical history, including past surgeries, current medications, and any chronic conditions.
- A thorough physical examination to assess overall health.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood tests to evaluate kidney and liver function, blood sugar levels, electrolytes, and complete blood count.
- Urine tests to check for kidney function and infections.
- Imaging Studies:
- Imaging studies such as chest X-rays, abdominal ultrasounds, and CT scans to assess the condition of internal organs and blood vessels.
- Cardiovascular Evaluation:
- Tests such as electrocardiograms (EKG), echocardiograms, and stress tests to assess heart health and ensure the patient can withstand the surgery.
- Consultations with Specialists:
- Endocrinologists, nephrologists, cardiologists, and other specialists as needed to evaluate and optimize the patient’s condition before surgery.
Psychosocial Evaluation
- Mental Health Assessment:
- Psychological evaluation to ensure the patient can handle the emotional and psychological aspects of transplantation.
- Assessing support systems, including family and friends, who can assist during recovery.
- Social Work Assessment:
- Evaluation by a social worker to address any social, financial, or logistical concerns related to the transplant process.
Lifestyle and Medical Adjustments
- Diet and Nutrition:
- Consult a dietitian to ensure proper nutrition and address any dietary needs or restrictions.
- Exercise:
- Implementing or maintaining a regular exercise regimen to improve physical fitness and overall health.
- Medications:
- Adjusting current medications as necessary and starting any new medications the transplant team prescribes.
- Ensuring up-to-date vaccinations to prevent infections.
- Smoking and Alcohol:
- Complete cessation of smoking and avoidance of alcohol to reduce surgical risks and promote healing.
Education and Planning
- Transplant Education:
- Attending educational sessions or meetings to learn about the transplant process, post-surgery care, and lifestyle changes.
- Understanding the risks, benefits, and long-term commitment required for a successful transplant.
- Financial Planning:
- Discuss the Pancreas Transplant costs in India associated with the transplant, including surgery, hospital stay, medications, and follow-up care.
- Exploring insurance coverage and financial assistance options.
- Know about Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India
- Living Arrangements and Support:
- Planning for post-surgery recovery, which may include arranging for a stay at a nearby facility or ensuring home accommodations are suitable for recovery.
- Organizing a support network of family and friends who can help with transportation, daily activities, and emotional support.
Listing and Waiting for a Donor
- Transplant Waiting List:
- Once deemed a suitable candidate, the patient is placed on the transplant waiting list.
- Regular follow-ups with the transplant team to monitor health status while waiting for a donor organ.
- Staying Ready:
- Keeping communication lines open with the transplant team to be ready for the surgery when a donor organ becomes available.
- Being prepared for potential last-minute calls for the transplant.
Pre-Surgery Preparation
- Pre-Admission Testing:
- The final round of tests and evaluations shortly before the scheduled surgery.
- Hospital Admission:
- Admission to the hospital, typically the day before or the day of the surgery, depends on the hospital’s protocols.
- Pre-Operative Instructions:
- Following specific instructions regarding fasting, medication adjustments, and pre-surgery hygiene as directed by the transplant team.
By thoroughly preparing for the pancreas transplant surgery, patients can optimize their chances for a successful procedure and smooth recovery.
What are the surgical procedures of Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
Pancreas transplant surgery is a complex procedure that involves several key steps, from organ procurement to the actual transplantation. Here’s an overview of the surgical procedures involved in a pancreas transplant:
1. Organ Procurement
- Donor Identification: The pancreas is obtained from a deceased donor who has been declared brain-dead but whose organs are still functioning.
- Organ Retrieval: The donor pancreas is surgically removed, often along with other organs such as the kidneys, under sterile conditions to prevent contamination.
- Organ Preservation: The pancreas is preserved in a special cold storage solution to maintain its viability until transplantation.
2. Pre-Surgery Preparation
- Patient Admission: The recipient is admitted to the hospital, and final pre-operative tests are conducted to ensure they are ready for surgery.
- Anesthesia: The patient is taken to the operating room and given general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free during the procedure.
3. Surgical Procedure
- Incision:
-
- A midline incision is made in the patient's abdomen to provide access to the abdominal cavity.
- Preparation of Recipient's Blood Vessels:
-
- The surgeon identifies and prepares the blood vessels that will be connected to the donor pancreas. This typically involves the iliac artery and vein.
- Pancreas Implantation:
-
- The donor pancreas, along with a segment of the donor’s small intestine or bladder, is placed into the recipient's lower abdomen.
- The blood vessels of the donor pancreas are connected to the recipient's iliac artery and vein to restore blood flow.
- Drainage of Pancreatic Secretions:
-
- Enteric Drainage: The donor’s portion of the small intestine is attached to the recipient’s small intestine or bladder to allow pancreatic enzymes to drain into the digestive system or bladder.
- Bladder Drainage: In some cases, the pancreatic enzymes are drained into the bladder. This method is less commonly used now due to complications associated with urinary drainage.
- Closure:
-
- Once the pancreas is in place and functioning, the surgeon closes the abdominal incision with sutures or staples.
What will be the poat care of Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
Post-Surgery Care
- Immediate Monitoring: The patient is taken to the intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring of vital signs, organ function, and any signs of complications.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: The patient is started on immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection of the transplanted pancreas.
- Pain Management: Pain relief measures are administered to ensure patient comfort during recovery.
- Fluid and Nutrition Management: Intravenous fluids and nutrition support are provided until the patient can resume normal eating.
Recovery and Follow-Up
- Hospital Stay: The typical hospital stay ranges from one to two weeks, depending on the patient's recovery progress and any complications.
- Monitoring for Rejection: Regular blood tests, imaging studies, and biopsies may be performed to monitor for signs of organ rejection.
- Long-Term Follow-Up: Lifelong follow-up care is required to monitor the function of the transplanted pancreas and to adjust immunosuppressive medications as needed.
What will be the success rate of Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
The success rate of pancreas transplant surgery can vary based on several factors, including the type of transplant, the recipient's health condition, and the expertise of the transplant center. Here are some general statistics and factors influencing the success rates:
General Success Rates
- Graft Survival:
- One-Year Graft Survival: Approximately 85-90% of transplanted pancreas are still functioning one year after the surgery.
- Five-Year Graft Survival: Around 70-75% of transplanted pancreas are still functioning five years after the surgery.
- Patient Survival:
- One-Year Patient Survival: About 95% of patients are alive one year after a pancreas transplant.
- Five-Year Patient Survival: Approximately 80-85% of patients are alive five years after the transplant.
Success Rates by Transplant Type
- Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney (SPK) Transplant:
- One-Year Graft Survival: Around 90%.
- Five-Year Graft Survival: Approximately 75%.
- Patient Survival: Similar to general statistics, with slight variations based on specific health conditions.
- Pancreas After Kidney (PAK) Transplant:
- One-Year Graft Survival: Around 85-88%.
- Five-Year Graft Survival: Approximately 70%.
- Patient Survival: Comparable to SPK transplants, though slightly lower in some cases.
- Pancreas Transplant Alone (PTA):
- One-Year Graft Survival: Approximately 80-85%.
- Five-Year Graft Survival: Around 60-65%.
- Patient Survival: Generally slightly lower than combined transplants due to the complexities of managing diabetes without concurrent kidney disease.
Factors Influencing Success Rates
- Recipient Health:
- Better overall health and fewer comorbid conditions increase the likelihood of a successful transplant.
- Transplant Center Experience:
- Centers with more experience and higher volumes of pancreas transplants tend to have better outcomes.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy:
- Effective management of immunosuppressive medications is crucial to prevent rejection and other complications.
- Post-Transplant Care:
- Regular follow-up visits, adherence to medication regimens, and monitoring for complications are vital for long-term success.
- Donor Factors:
- The age and health of the donor, as well as the condition of the donor's pancreas, can affect transplant outcomes.
Long-Term Benefits
- Improved Quality of Life:
- Many patients experience significant improvements in their quality of life, with better blood sugar control and reduced complications from diabetes.
- Insulin Independence:
- A majority of successful pancreas transplant recipients achieve insulin independence, eliminating the need for insulin injections.
- Reduced Diabetes Complications:
- Long-term benefits include a lower risk of diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular issues.
Challenges and Considerations
- Risk of Rejection:
- Despite advances in immunosuppressive therapy, rejection remains a significant challenge.
- Side Effects of Medications:
- Immunosuppressive drugs can have serious side effects, including increased susceptibility to infections and certain cancers.
- Financial Costs:
- The cost of the surgery, hospital stay, medications, and long-term follow-up can be substantial.
Overall, while pancreas transplant surgery offers significant benefits for patients with severe diabetes, it is associated with considerable risks and requires a lifelong commitment to medical care. The decision to undergo a pancreas transplant should be made in close consultation with a specialized transplant team.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
General Information
1. What is a pancreas transplant?
- A pancreas transplant is a surgical procedure where a healthy pancreas from a deceased donor is transplanted into a person whose pancreas no longer functions properly, primarily to treat severe cases of type 1 diabetes.
2. Who is a candidate for a pancreas transplant?
- Candidates are typically individuals with type 1 diabetes who have severe complications, such as frequent episodes of hypoglycemia, hypoglycemia unawareness, or end-stage renal disease. In some cases, patients with type 2 diabetes may also be considered.
3. What are the different types of pancreas transplants?
- There are three main types:
- Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney (SPK) Transplant: For patients with both diabetes and kidney failure.
- Pancreas After Kidney (PAK) Transplant: For patients who have already received a kidney transplant.
- Pancreas Transplant Alone (PTA): For patients with severe diabetes complications but normal kidney function.
Surgery and Recovery
4. How long does the pancreas transplant surgery take?
- The surgery typically takes about 4-6 hours.
5. What is the recovery process like?
- Recovery involves a hospital stay of about 1-2 weeks, followed by regular follow-up visits. Patients need to take immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection and adhere to a strict post-operative care regimen.
6. What are the potential complications of pancreas transplant surgery?
- Complications can include infection, bleeding, blood clots, pancreatitis, rejection of the transplanted pancreas, and side effects from immunosuppressive medications.
Success Rates and Benefits
7. What is the success rate of pancreas transplants?
- One-year graft survival rates are about 85-90%, and five-year graft survival rates are around 70-75%. Patient survival rates are about 95% at one year and 80-85% at five years.
8. What are the benefits of a pancreas transplant?
- Benefits include achieving insulin independence, improved blood sugar control, and a reduction in diabetes-related complications, leading to an enhanced quality of life.
Lifestyle and Long-Term Care
9. What lifestyle changes are needed after a pancreas transplant?
- Patients must adhere to a lifelong regimen of immunosuppressive medications, attend regular follow-up appointments, maintain a healthy diet, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and manage stress.
10. Can I live a normal life after a pancreas transplant?
- Many patients can lead a relatively normal life with significant improvements in their quality of life and diabetes management. However, lifelong medical follow-up and treatment adherence are crucial.
Financial and Logistical Considerations
11. How much does a pancreas transplant cost in India?
- The Pancreas transplant cost varies widely depending on the country, hospital, and individual case. It typically includes expenses for surgery, hospitalization, medications, and long-term follow-up care. Insurance coverage and financial assistance options should be explored.
12. How long is the waiting period for a pancreas transplant?
- The waiting period can vary significantly based on factors like blood type, organ availability, and the patient's health condition. It can range from a few months to several years.
13. How do I prepare for a pancreas transplant?
- Preparation involves a comprehensive medical evaluation, lifestyle adjustments, and planning for post-surgery care. Patients need to follow specific instructions from their transplant team to optimize their health before surgery.
Other Considerations
14. Can I have other transplants in conjunction with a pancreas transplant?
- Yes, simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants are common for patients with both diabetes and kidney failure.
15. What happens if the transplanted pancreas fails?
- If the transplanted pancreas fails, the patient may need to resume insulin therapy and could be considered for another transplant, depending on their health and specific circumstances.
16. Where can I find more information and support?
- Patients can find information and support through their transplant center, healthcare providers, and organizations such as the American Diabetes Association and the International Pancreas Transplant Registry.
Always consult with a specialized transplant team to get personalized advice and information regarding pancreas transplant surgery.
Top Doctors
Top Hospitals
PANCREAS TRANSPLANT SURGERY COST IN INDIA

Duration of Treatment
5 to 6 hours
Days of Stay
1 to 5 month
Anesthesia
General Anesthesia
Cost
20000 USD
How Much Does Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India?
Are we looking for Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India at an affordable cost? Here, we answer the question and explain how to choose the top doctors for better results.
We have shortlisted the list of the best top Pancreas Transplant Surgery Hospitals and Surgeons based on Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of surgeons, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India: starting from 20000 to 30000 USD.
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD (as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day)
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day).
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will be planned after the fresh evaluation reports.
- In India, Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India can vary as per the diagnosis, patient's conditions, Bariatric surgeon experience, Implant quality, hospital facilities, and city.
- To make an appointment, learn more about the Gastric, read the information below, or call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782. Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
What is Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
A pancreas transplant is a surgical procedure to implant a healthy pancreas from a deceased donor into a person whose pancreas no longer functions properly. The primary purpose of a pancreas transplant is to treat type 1 diabetes, a condition where the pancreas cannot produce insulin. Here are the main points about pancreas transplant surgery:
Indications
- Type 1 Diabetes: Most commonly performed for people with type 1 diabetes who have severe complications, such as hypoglycemia unawareness, or kidney failure.
- Type 2 Diabetes: In rare cases, it can be performed for type 2 diabetes if the patient meets specific criteria.
Types of Pancreas Transplants
- Pancreas Alone: For patients with severe diabetes without kidney disease.
- Pancreas-Kidney Transplant: For patients with both diabetes and kidney failure.
- Pancreas After Kidney Transplant: For patients who have already had a kidney transplant and later receive a pancreas transplant.
symptoms
Who can have a pancreas transplant?
-
Age: Generally, candidates are between 18 and 65, but this can vary based on individual health status.
- Overall Health: Candidates should be healthy enough to undergo major surgery and handle the immunosuppressive medications required after transplantation.
- Absence of Contraindications: Candidates should not have significant health issues such as active infections, recent cancer, or severe cardiovascular disease.
- Compliance: Candidates must demonstrate the ability to adhere to the rigorous post-transplant care regimen, including taking medications as prescribed and attending regular follow-up appointments.
Evaluation Process
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Comprehensive evaluation to assess the patient's overall health and suitability for surgery.
- Psychosocial Evaluation: Assessment to ensure the patient can handle transplantation's psychological and social demands.
- Laboratory and Imaging Tests: To assess organ function and overall health status.
- Consultations: With specialists such as endocrinologists, nephrologists, and transplant surgeons.
Relative Contraindications
- Obesity: Excessive weight can complicate surgery and recovery.
- Substance Abuse: Active substance abuse is typically a contraindication.
- Non-compliance: History of non-compliance with medical treatments.
risk factors
What is the Risk Factor of Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
Pancreas transplant surgery carries several risks, which can be categorized into short-term and long-term complications. Here are the primary risk factors:
Short-Term Risks
- Surgical Complications:
- Bleeding: Significant blood loss during or after surgery.
- Infection: Risk of infection at the surgical site or within the abdomen.
- Blood Clots: Formation of clots in the blood vessels of the transplanted pancreas.
- Organ Rejection:
- Acute Rejection: The body's immune system attacks the new pancreas, which can occur within weeks to months after transplantation.
- Chronic Rejection: A slower, ongoing immune response that can lead to gradual loss of pancreas function over time.
- Pancreatitis:
- Inflammation of the transplanted pancreas can cause abdominal pain and digestive issues.
- Graft Thrombosis:
- Blood clots can form in the blood vessels supplying the new pancreas, leading to graft failure.
- Delayed Graft Function:
- The transplanted pancreas may not work immediately, requiring additional medical support.
Long-Term Risks
- Infections:
- Increased risk of infections due to the lifelong need for immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection.
- Immunosuppressive Medication Side Effects:
- Kidney Damage: Some immunosuppressive drugs can harm the kidneys.
- High Blood Pressure: Immunosuppressants can cause hypertension.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels are common.
- Diabetes: Some patients may develop diabetes post-transplant.
- Increased Cancer Risk: Long-term immunosuppression can increase the risk of certain cancers.
- Recurrence of Diabetes:
- While rare, diabetes can recur in the transplanted pancreas.
- Psychosocial Issues:
- The emotional and psychological impact of transplantation, including anxiety, depression, and stress related to the need for ongoing medical care.
Other Considerations
- Organ Availability:
- The scarcity of suitable donor organs can lead to long waiting times, during which the patient's condition may deteriorate.
- Quality of Life:
- While many patients experience significant improvements, the need for continuous medical follow-up and potential complications can impact quality of life.
- Financial Costs:
- Surgery, hospitalization, medications, and long-term follow-up care costs can be substantial.
Mitigating Risks
- Thorough Evaluation: Comprehensive pre-transplant evaluation to ensure candidates are suitable.
- Experienced Surgical Team: Having surgery performed by a skilled and experienced transplant team.
- Post-Operative Care: Close monitoring and adherence to medical recommendations post-surgery.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support overall health and the function of the transplanted organ.
Patients considering a pancreas transplant should discuss these risks and benefits in detail with their transplant team to make an informed decision.
preparation
What is the preparation needed before Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
Preparing for a pancreas transplant surgery involves several steps to ensure that the patient is in optimal health and ready for the procedure. Here are the key aspects of the preparation process:
Medical Evaluation
- Comprehensive Medical History and Physical Examination:
- A detailed review of the patient's medical history, including past surgeries, current medications, and any chronic conditions.
- A thorough physical examination to assess overall health.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood tests to evaluate kidney and liver function, blood sugar levels, electrolytes, and complete blood count.
- Urine tests to check for kidney function and infections.
- Imaging Studies:
- Imaging studies such as chest X-rays, abdominal ultrasounds, and CT scans to assess the condition of internal organs and blood vessels.
- Cardiovascular Evaluation:
- Tests such as electrocardiograms (EKG), echocardiograms, and stress tests to assess heart health and ensure the patient can withstand the surgery.
- Consultations with Specialists:
- Endocrinologists, nephrologists, cardiologists, and other specialists as needed to evaluate and optimize the patient’s condition before surgery.
Psychosocial Evaluation
- Mental Health Assessment:
- Psychological evaluation to ensure the patient can handle the emotional and psychological aspects of transplantation.
- Assessing support systems, including family and friends, who can assist during recovery.
- Social Work Assessment:
- Evaluation by a social worker to address any social, financial, or logistical concerns related to the transplant process.
Lifestyle and Medical Adjustments
- Diet and Nutrition:
- Consult a dietitian to ensure proper nutrition and address any dietary needs or restrictions.
- Exercise:
- Implementing or maintaining a regular exercise regimen to improve physical fitness and overall health.
- Medications:
- Adjusting current medications as necessary and starting any new medications the transplant team prescribes.
- Ensuring up-to-date vaccinations to prevent infections.
- Smoking and Alcohol:
- Complete cessation of smoking and avoidance of alcohol to reduce surgical risks and promote healing.
Education and Planning
- Transplant Education:
- Attending educational sessions or meetings to learn about the transplant process, post-surgery care, and lifestyle changes.
- Understanding the risks, benefits, and long-term commitment required for a successful transplant.
- Financial Planning:
- Discuss the Pancreas Transplant costs in India associated with the transplant, including surgery, hospital stay, medications, and follow-up care.
- Exploring insurance coverage and financial assistance options.
- Know about Pancreas Transplant Surgery Cost in India
- Living Arrangements and Support:
- Planning for post-surgery recovery, which may include arranging for a stay at a nearby facility or ensuring home accommodations are suitable for recovery.
- Organizing a support network of family and friends who can help with transportation, daily activities, and emotional support.
Listing and Waiting for a Donor
- Transplant Waiting List:
- Once deemed a suitable candidate, the patient is placed on the transplant waiting list.
- Regular follow-ups with the transplant team to monitor health status while waiting for a donor organ.
- Staying Ready:
- Keeping communication lines open with the transplant team to be ready for the surgery when a donor organ becomes available.
- Being prepared for potential last-minute calls for the transplant.
Pre-Surgery Preparation
- Pre-Admission Testing:
- The final round of tests and evaluations shortly before the scheduled surgery.
- Hospital Admission:
- Admission to the hospital, typically the day before or the day of the surgery, depends on the hospital’s protocols.
- Pre-Operative Instructions:
- Following specific instructions regarding fasting, medication adjustments, and pre-surgery hygiene as directed by the transplant team.
By thoroughly preparing for the pancreas transplant surgery, patients can optimize their chances for a successful procedure and smooth recovery.
procedure
What are the surgical procedures of Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
Pancreas transplant surgery is a complex procedure that involves several key steps, from organ procurement to the actual transplantation. Here’s an overview of the surgical procedures involved in a pancreas transplant:
1. Organ Procurement
- Donor Identification: The pancreas is obtained from a deceased donor who has been declared brain-dead but whose organs are still functioning.
- Organ Retrieval: The donor pancreas is surgically removed, often along with other organs such as the kidneys, under sterile conditions to prevent contamination.
- Organ Preservation: The pancreas is preserved in a special cold storage solution to maintain its viability until transplantation.
2. Pre-Surgery Preparation
- Patient Admission: The recipient is admitted to the hospital, and final pre-operative tests are conducted to ensure they are ready for surgery.
- Anesthesia: The patient is taken to the operating room and given general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free during the procedure.
3. Surgical Procedure
- Incision:
-
- A midline incision is made in the patient's abdomen to provide access to the abdominal cavity.
- Preparation of Recipient's Blood Vessels:
-
- The surgeon identifies and prepares the blood vessels that will be connected to the donor pancreas. This typically involves the iliac artery and vein.
- Pancreas Implantation:
-
- The donor pancreas, along with a segment of the donor’s small intestine or bladder, is placed into the recipient's lower abdomen.
- The blood vessels of the donor pancreas are connected to the recipient's iliac artery and vein to restore blood flow.
- Drainage of Pancreatic Secretions:
-
- Enteric Drainage: The donor’s portion of the small intestine is attached to the recipient’s small intestine or bladder to allow pancreatic enzymes to drain into the digestive system or bladder.
- Bladder Drainage: In some cases, the pancreatic enzymes are drained into the bladder. This method is less commonly used now due to complications associated with urinary drainage.
- Closure:
-
- Once the pancreas is in place and functioning, the surgeon closes the abdominal incision with sutures or staples.
post procedure
What will be the poat care of Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
Post-Surgery Care
- Immediate Monitoring: The patient is taken to the intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring of vital signs, organ function, and any signs of complications.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: The patient is started on immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection of the transplanted pancreas.
- Pain Management: Pain relief measures are administered to ensure patient comfort during recovery.
- Fluid and Nutrition Management: Intravenous fluids and nutrition support are provided until the patient can resume normal eating.
Recovery and Follow-Up
- Hospital Stay: The typical hospital stay ranges from one to two weeks, depending on the patient's recovery progress and any complications.
- Monitoring for Rejection: Regular blood tests, imaging studies, and biopsies may be performed to monitor for signs of organ rejection.
- Long-Term Follow-Up: Lifelong follow-up care is required to monitor the function of the transplanted pancreas and to adjust immunosuppressive medications as needed.
success rate
What will be the success rate of Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
The success rate of pancreas transplant surgery can vary based on several factors, including the type of transplant, the recipient's health condition, and the expertise of the transplant center. Here are some general statistics and factors influencing the success rates:
General Success Rates
- Graft Survival:
- One-Year Graft Survival: Approximately 85-90% of transplanted pancreas are still functioning one year after the surgery.
- Five-Year Graft Survival: Around 70-75% of transplanted pancreas are still functioning five years after the surgery.
- Patient Survival:
- One-Year Patient Survival: About 95% of patients are alive one year after a pancreas transplant.
- Five-Year Patient Survival: Approximately 80-85% of patients are alive five years after the transplant.
Success Rates by Transplant Type
- Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney (SPK) Transplant:
- One-Year Graft Survival: Around 90%.
- Five-Year Graft Survival: Approximately 75%.
- Patient Survival: Similar to general statistics, with slight variations based on specific health conditions.
- Pancreas After Kidney (PAK) Transplant:
- One-Year Graft Survival: Around 85-88%.
- Five-Year Graft Survival: Approximately 70%.
- Patient Survival: Comparable to SPK transplants, though slightly lower in some cases.
- Pancreas Transplant Alone (PTA):
- One-Year Graft Survival: Approximately 80-85%.
- Five-Year Graft Survival: Around 60-65%.
- Patient Survival: Generally slightly lower than combined transplants due to the complexities of managing diabetes without concurrent kidney disease.
Factors Influencing Success Rates
- Recipient Health:
- Better overall health and fewer comorbid conditions increase the likelihood of a successful transplant.
- Transplant Center Experience:
- Centers with more experience and higher volumes of pancreas transplants tend to have better outcomes.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy:
- Effective management of immunosuppressive medications is crucial to prevent rejection and other complications.
- Post-Transplant Care:
- Regular follow-up visits, adherence to medication regimens, and monitoring for complications are vital for long-term success.
- Donor Factors:
- The age and health of the donor, as well as the condition of the donor's pancreas, can affect transplant outcomes.
Long-Term Benefits
- Improved Quality of Life:
- Many patients experience significant improvements in their quality of life, with better blood sugar control and reduced complications from diabetes.
- Insulin Independence:
- A majority of successful pancreas transplant recipients achieve insulin independence, eliminating the need for insulin injections.
- Reduced Diabetes Complications:
- Long-term benefits include a lower risk of diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular issues.
Challenges and Considerations
- Risk of Rejection:
- Despite advances in immunosuppressive therapy, rejection remains a significant challenge.
- Side Effects of Medications:
- Immunosuppressive drugs can have serious side effects, including increased susceptibility to infections and certain cancers.
- Financial Costs:
- The cost of the surgery, hospital stay, medications, and long-term follow-up can be substantial.
Overall, while pancreas transplant surgery offers significant benefits for patients with severe diabetes, it is associated with considerable risks and requires a lifelong commitment to medical care. The decision to undergo a pancreas transplant should be made in close consultation with a specialized transplant team.
faqs from doctor
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Pancreas Transplant Surgery?
General Information
1. What is a pancreas transplant?
- A pancreas transplant is a surgical procedure where a healthy pancreas from a deceased donor is transplanted into a person whose pancreas no longer functions properly, primarily to treat severe cases of type 1 diabetes.
2. Who is a candidate for a pancreas transplant?
- Candidates are typically individuals with type 1 diabetes who have severe complications, such as frequent episodes of hypoglycemia, hypoglycemia unawareness, or end-stage renal disease. In some cases, patients with type 2 diabetes may also be considered.
3. What are the different types of pancreas transplants?
- There are three main types:
- Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney (SPK) Transplant: For patients with both diabetes and kidney failure.
- Pancreas After Kidney (PAK) Transplant: For patients who have already received a kidney transplant.
- Pancreas Transplant Alone (PTA): For patients with severe diabetes complications but normal kidney function.
Surgery and Recovery
4. How long does the pancreas transplant surgery take?
- The surgery typically takes about 4-6 hours.
5. What is the recovery process like?
- Recovery involves a hospital stay of about 1-2 weeks, followed by regular follow-up visits. Patients need to take immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection and adhere to a strict post-operative care regimen.
6. What are the potential complications of pancreas transplant surgery?
- Complications can include infection, bleeding, blood clots, pancreatitis, rejection of the transplanted pancreas, and side effects from immunosuppressive medications.
Success Rates and Benefits
7. What is the success rate of pancreas transplants?
- One-year graft survival rates are about 85-90%, and five-year graft survival rates are around 70-75%. Patient survival rates are about 95% at one year and 80-85% at five years.
8. What are the benefits of a pancreas transplant?
- Benefits include achieving insulin independence, improved blood sugar control, and a reduction in diabetes-related complications, leading to an enhanced quality of life.
Lifestyle and Long-Term Care
9. What lifestyle changes are needed after a pancreas transplant?
- Patients must adhere to a lifelong regimen of immunosuppressive medications, attend regular follow-up appointments, maintain a healthy diet, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and manage stress.
10. Can I live a normal life after a pancreas transplant?
- Many patients can lead a relatively normal life with significant improvements in their quality of life and diabetes management. However, lifelong medical follow-up and treatment adherence are crucial.
Financial and Logistical Considerations
11. How much does a pancreas transplant cost in India?
- The Pancreas transplant cost varies widely depending on the country, hospital, and individual case. It typically includes expenses for surgery, hospitalization, medications, and long-term follow-up care. Insurance coverage and financial assistance options should be explored.
12. How long is the waiting period for a pancreas transplant?
- The waiting period can vary significantly based on factors like blood type, organ availability, and the patient's health condition. It can range from a few months to several years.
13. How do I prepare for a pancreas transplant?
- Preparation involves a comprehensive medical evaluation, lifestyle adjustments, and planning for post-surgery care. Patients need to follow specific instructions from their transplant team to optimize their health before surgery.
Other Considerations
14. Can I have other transplants in conjunction with a pancreas transplant?
- Yes, simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants are common for patients with both diabetes and kidney failure.
15. What happens if the transplanted pancreas fails?
- If the transplanted pancreas fails, the patient may need to resume insulin therapy and could be considered for another transplant, depending on their health and specific circumstances.
16. Where can I find more information and support?
- Patients can find information and support through their transplant center, healthcare providers, and organizations such as the American Diabetes Association and the International Pancreas Transplant Registry.
Always consult with a specialized transplant team to get personalized advice and information regarding pancreas transplant surgery.

























