Duration of Treatment
15 Days
Days of Stay
2 days in Hospital
Anesthesia
No Need
Cost
7000 to 12000 USD
Stem cell transplant for arthritis Cost in India
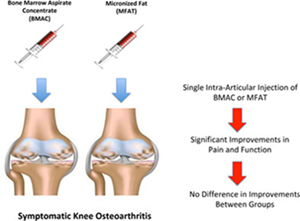
Stem cell transplant for arthritis is an emerging treatment aimed at repairing and regenerating damaged joint tissues, particularly cartilage, using stem cells. This therapy is considered especially for conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, where conventional treatments may not provide sufficient relief or halt disease progression.
What is Stem Cell Transplant in Arthritis?
Stem cell therapy for arthritis involves injecting stem cells into the affected joints to promote healing and regeneration of the damaged tissues. Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including cartilage, bone, and muscle cells, which makes them ideal for repairing joint damage.
Types of Stem Cells Used:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs):
- Derived from bone marrow, adipose (fat) tissue, or umbilical cord tissue.
- Known for their ability to differentiate into cartilage and bone cells.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs):
- Typically derived from bone marrow or peripheral blood.
- More commonly used in treatments for blood-related disorders but can also aid in tissue regeneration.
Benefits:
- Pain Reduction: Decreased inflammation and pain in the affected joints.
- Improved Function: Enhanced joint mobility and function.
- Tissue Regeneration: Potential regeneration of cartilage and other joint tissues.
- Reduced Need for Surgery: May delay or prevent the need for joint replacement surgery.
The cost of stem cell transplant therapy for arthritis in India can vary widely based on several factors, including the type of stem cells used, the healthcare facility, the city, and the specific treatment protocol. Here are some general estimates and factors that influence the cost:
General Stem cell transplant for arthritis Cost in India:
-
Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells:
- Cost: 15000 to 20000 USD per treatment session.
-
Adipose (Fat) Tissue-Derived Stem Cells:
- Cost: 7000 to 8000 USD per treatment session.
-
Umbilical Cord-Derived Stem Cells:
- Cost: 8500 to 15000 USD per treatment session.
Factors Influencing the Cost:
- Type of Stem Cells: Different sources of stem cells (bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord) have different extraction and processing costs.
- Healthcare Facility: Stem cell therapy in India Costs are generally higher in reputed private hospitals compared to smaller clinics or government hospitals.
- City: Metropolitan cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, and Chennai may have higher costs compared to smaller cities or towns.
- Treatment Protocol: The number of stem cell injections required, additional therapies, and follow-up care can influence the overall cost.
- Surgeon’s Expertise: Experienced and renowned specialists may charge higher fees.
- Preoperative and Postoperative Care: Includes consultation fees, diagnostic tests, medications, and follow-up visits.
Insurance Coverage:
- Many health insurance policies in India do not yet cover stem cell therapy as it is considered experimental or investigational. It is advisable to check with your insurance provider for specific coverage details.
Consultation and Diagnostic Tests:
- Initial consultation fees and diagnostic tests (such as MRI, X-rays, and blood tests) may cost between 5,000 to 15,000, depending on the hospital and location.
Additional Costs:
- Travel and Accommodation: For patients traveling from other cities or countries, travel and accommodation costs can add to the overall expense.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up visits to monitor progress and additional treatments, if necessary.
For the most accurate and personalized Stem cell transplant for arthritis Cost in India estimate, it’s best to contact specific hospitals or stem cell therapy centers directly. They can provide detailed information based on individual cases and requirements.
Stem cell therapy for arthritis aims to alleviate symptoms and improve joint function by promoting the regeneration of damaged tissues. While stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, patients may experience various symptoms or side effects during and after the treatment. Here are some common symptoms and side effects associated with stem cell therapy for arthritis:
Common Symptoms and Side Effects:
- Injection Site Reactions:
- Pain and Discomfort: Mild to moderate pain or discomfort at the injection site.
- Swelling: Temporary swelling around the injection area.
- Redness and Bruising: Localized redness and bruising, which usually resolve within a few days.
- Systemic Reactions:
- Fever: Low-grade fever can occur as an immune response to the treatment.
- Fatigue: Temporary fatigue or tiredness following the procedure.
- Inflammation and Soreness:
- Joint Inflammation: Mild inflammation and soreness in the treated joint, which typically subside within a few days to a week.
- Allergic Reactions:
- Rare: Allergic reactions to the materials used in the procedure or the stem cells themselves are rare but possible.
- Infection:
- Risk: Although rare, there is a risk of infection at the injection site. Signs of infection include increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth, and fever.
Expected Improvements:
- Pain Relief:
- Reduced Joint Pain: Many patients experience a reduction in joint pain within weeks to months after the treatment.
- Improved Mobility:
- Enhanced Joint Function: Improved range of motion and joint function, allowing for better mobility and physical activity.
- Cartilage Regeneration:
- Tissue Repair: Stem cells can promote the regeneration of damaged cartilage and other joint tissues, leading to structural improvements in the joint.
- Reduced Inflammation:
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce chronic inflammation in the affected joints
Risks and Considerations:
- Infection: Risk of infection at the injection site.
- Allergic Reaction: Possible allergic reactions to the injected materials.
- Variable Results: Efficacy can vary from patient to patient.
- Cost: Stem cell therapy can be expensive and is not always covered by insurance.
Current Status and Research:
- Clinical Trials: Ongoing research and clinical trials are exploring the effectiveness and safety of stem cell therapy for arthritis.
- Regulatory Approval: Stem cell therapies are still under investigation and may not be widely approved or available for arthritis treatment in all regions.
Consultation and Eligibility:
- Consultation: A detailed consultation with an orthopedic specialist or a rheumatologist is necessary to determine if a patient is a good candidate for stem cell therapy.
- Eligibility: Factors like the type and severity of arthritis, overall health, and previous treatments are considered.
Stem cell therapy for arthritis holds promise but is still an evolving field. It’s essential to have realistic expectations and to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare provider.
Preparation for stem cell therapy for arthritis involves several steps to ensure the patient is a suitable candidate and to optimize the chances of a successful outcome. Here are the key steps in the preparation process:
1. Consultation and Evaluation:
- Initial Consultation: Schedule an appointment with a specialized orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist experienced in stem cell therapy.
- Medical History: Provide a detailed medical history, including current medications, previous treatments, and any underlying health conditions.
- Physical Examination: Undergo a thorough physical examination to assess the severity of arthritis and overall joint function.
2. Diagnostic Tests:
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound may be conducted to evaluate the extent of joint damage and guide the treatment plan.
- Blood Tests: Routine blood tests to check for any underlying conditions that could affect the treatment.
- Joint Fluid Analysis: In some cases, a sample of joint fluid may be analyzed to rule out infections or other conditions.
3. Determining Candidacy:
- Eligibility: The doctor will determine if the patient is a suitable candidate for stem cell therapy based on the type and severity of arthritis, overall health, and previous treatments.
- Alternative Treatments: Discuss alternative treatment options and compare them with stem cell therapy to make an informed decision.
4. Pre-Treatment Instructions:
- Medications: Review and possibly adjust current medications. Patients may need to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or anti-inflammatory drugs, before the procedure.
- Supplements: Inform the doctor about any supplements being taken, as some may need to be discontinued prior to treatment.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to optimize overall health and the body’s response to the treatment.
5. Preparation for the Procedure:
- Fasting: Follow any fasting instructions provided by the doctor, especially if sedation or anesthesia will be used during the procedure.
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated in the days leading up to the procedure.
- Arrangements: Arrange for transportation to and from the medical facility, as patients may not be able to drive immediately after the procedure.
6. The Day of the Procedure:
- Arrival: Arrive at the medical facility as instructed, typically a few hours before the scheduled procedure.
- Consent: Sign any necessary consent forms after discussing the procedure, risks, and benefits with the healthcare provider.
- Comfort: Wear comfortable clothing and avoid wearing jewelry or accessories that may interfere with the procedure.
7. During the Procedure:
- Anesthesia: Depending on the type of stem cell therapy, local anesthesia, sedation, or general anesthesia may be used to ensure comfort during the procedure.
- Stem Cell Harvesting:
- Bone Marrow Aspiration: If bone marrow-derived stem cells are used, a needle is inserted into the pelvic bone to extract bone marrow.
- Adipose Tissue Extraction: If adipose (fat) tissue-derived stem cells are used, a small amount of fat is extracted from areas like the abdomen or thigh.
- Umbilical Cord Tissue: Pre-prepared stem cells from umbilical cord tissue are used without the need for harvesting from the patient.
- Stem Cell Processing: The harvested stem cells are processed and concentrated in a laboratory setting to prepare them for injection.
- Injection: The processed stem cells are injected directly into the affected joint(s) using imaging guidance (such as ultrasound) to ensure precise placement.
8. Post-Procedure Care:
- Observation: Patients are typically observed for a short period after the procedure to monitor for any immediate reactions.
- Pain Management: Mild pain or discomfort at the injection site can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, as advised by the doctor.
- Activity Restrictions: Follow any activity restrictions or guidelines provided by the healthcare provider, such as avoiding strenuous activities for a few days.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Schedule and attend follow-up appointments to monitor progress and assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
9. Long-Term Care:
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can help improve joint function and enhance the benefits of stem cell therapy.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management, to support joint health and overall well-being.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor symptoms and report any changes or concerns to the healthcare provider to ensure timely interventions if needed.
By carefully following these preparation steps, patients can optimize their outcomes from stem cell therapy for arthritis and improve their chances of achieving pain relief and improved joint function.
The success of stem cell therapy for arthritis varies depending on several factors, including the type of arthritis, the severity of the condition, the source of stem cells used, and the individual patient's health. Here's a breakdown of what to consider regarding the success and outcomes of stem cell therapy for arthritis:
Factors Influencing Success:
- Type of Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): Stem cell therapy has shown promising results in treating osteoarthritis, especially in the knees and hips. Success rates can vary, but many patients report improved pain relief and joint function.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): The effectiveness of stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis is still under investigation. RA often requires more complex approaches due to its systemic nature and the presence of joint deformities.
- Severity of the Condition:
- Early-Stage Arthritis: Patients with early-stage arthritis or less severe joint damage often experience better outcomes compared to those with advanced or end-stage arthritis.
- Advanced Arthritis: Stem cell therapy may provide limited relief in cases of severe joint damage or where there is significant bone loss or deformity.
- Type of Stem Cells Used:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord tissue, MSCs are commonly used and have shown positive results in many clinical studies.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs): More commonly used for blood disorders, their role in arthritis is less established.
- Source of Stem Cells:
- Autologous Stem Cells: Using the patient’s own stem cells (from bone marrow or adipose tissue) generally has a lower risk of rejection and complications.
- Allogeneic Stem Cells: Stem cells from donors (e.g., umbilical cord tissue) may be effective but can involve additional considerations related to donor compatibility and processing.
- Individual Patient Factors:
- Overall Health: General health, including the presence of other medical conditions, can impact the success of the therapy.
- Compliance: Adherence to post-treatment care, including physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, plays a crucial role in achieving optimal outcomes.
Expected Outcomes:
- Pain Relief:
- Many patients experience a significant reduction in joint pain and discomfort after stem cell therapy. Pain relief can often begin within a few weeks and may continue to improve over several months.
- Improved Joint Function:
- Enhanced joint mobility and function are commonly reported. Patients often find it easier to perform daily activities and engage in physical exercise.
- Cartilage Regeneration:
- Stem cell therapy aims to regenerate damaged cartilage. While some studies show evidence of cartilage repair or regeneration, the extent of this repair can vary.
- Reduced Inflammation:
- Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties that can help decrease joint inflammation, contributing to overall symptom relief.
Clinical Research and Evidence:
- Clinical Trials: Ongoing research and clinical trials continue to evaluate the effectiveness of stem cell therapy for arthritis. Some studies have reported positive outcomes, while others highlight the need for further research to confirm long-term benefits and safety.
- Success Rates: Success rates can vary widely. Some studies report significant improvements in symptoms for a majority of patients, while others show more modest results.
Considerations and Limitations:
- Variable Results: Results can be inconsistent, with some patients experiencing significant benefits and others seeing minimal improvement.
- Long-Term Effects: The long-term effects of stem cell therapy are still being studied. Patients should discuss potential outcomes and risks with their healthcare provider.
- Cost and Accessibility: Stem cell therapy can be expensive and may not be covered by insurance. Patients should consider the financial implications and explore available options.
Consultation and Personalized Approach:
- Specialist Consultation: It is important to consult with a specialist experienced in stem cell therapy for arthritis to determine if the treatment is suitable and to discuss expected outcomes.
- Personalized Treatment Plan: Each patient’s treatment plan should be tailored to their specific condition, health status, and treatment goals.
Overall, while stem cell therapy for arthritis shows promise, it is essential to have realistic expectations and to work closely with healthcare providers to assess the potential benefits and risks based on individual circumstances.
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about stem cell therapy for arthritis:
1. What is stem cell therapy for arthritis?
Answer: Stem cell therapy for arthritis involves injecting stem cells into affected joints to promote tissue repair and regeneration. The goal is to reduce pain, improve joint function, and potentially regenerate damaged cartilage.
2. How does stem cell therapy work for arthritis?
Answer: Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including cartilage and bone cells. When injected into damaged joints, they can help repair and regenerate tissues, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain.
3. What types of stem cells are used in arthritis treatment?
Answer: Commonly used stem cells include:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Typically derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord tissue.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs): More commonly used for blood-related disorders, but may also have applications in arthritis.
4. Is stem cell therapy safe?
Answer: Stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, but it carries some risks, such as infection, allergic reactions, and pain at the injection site. It is important to discuss potential risks with a healthcare provider and choose a reputable facility.
5. How effective is stem cell therapy for arthritis?
Answer: The effectiveness of stem cell therapy varies. Many patients experience significant pain relief and improved joint function, especially in early-stage arthritis. However, results can be variable, and ongoing research is needed to confirm long-term benefits and safety.
6. How long does it take to see results from stem cell therapy?
Answer: Patients may begin to notice improvements in pain and joint function within a few weeks to months after the procedure. Full benefits may take several months to become evident.
7. How is the stem cell therapy procedure performed?
Answer: The procedure typically involves:
- Harvesting: Stem cells are collected from the patient’s bone marrow, adipose tissue, or obtained from a donor source.
- Processing: The collected stem cells are processed and concentrated.
- Injection: The processed stem cells are injected into the affected joint using imaging guidance to ensure precise placement.
8. What are the potential side effects of stem cell therapy?
Answer: Common side effects include mild pain or discomfort at the injection site, swelling, and redness. Rare but possible side effects include infection and allergic reactions. Patients should monitor for any unusual symptoms and report them to their healthcare provider.
9. How should I prepare for stem cell therapy?
Answer: Preparation may include:
- Medical Evaluation: Undergoing a thorough medical evaluation and diagnostic tests.
- Medication Review: Discussing current medications with your doctor and possibly adjusting them.
- Pre-Procedure Instructions: Following fasting or other pre-procedure instructions as advised by your healthcare provider.
10. What is the cost of stem cell therapy for arthritis?
Answer: The cost varies widely depending on factors such as the type of stem cells used, the healthcare facility, and the city. On average, the cost ranges from ?1,50,000 to ?7,00,000 per treatment session. It is advisable to check with specific hospitals or clinics for accurate pricing.
11. Is stem cell therapy covered by insurance?
Answer: Many insurance policies do not cover stem cell therapy as it is often considered experimental or investigational. Patients should check with their insurance provider for coverage details and explore financing options if needed.
12. How many sessions of stem cell therapy will I need?
Answer: The number of sessions required can vary based on the individual’s condition and response to treatment. Some patients may benefit from a single session, while others may require multiple sessions.
13. What should I expect after the procedure?
Answer: After the procedure, you may experience mild pain or swelling at the injection site. It is important to follow post-procedure care instructions, including activity restrictions and follow-up appointments, to monitor progress and ensure optimal outcomes.
14. How do I choose a facility for stem cell therapy?
Answer: Choose a reputable facility with experienced specialists in stem cell therapy. Look for accreditation, review patient testimonials, and consult with the healthcare provider to ensure the facility meets your needs and expectations.
15. What are the long-term outcomes of stem cell therapy for arthritis?
Answer: Long-term outcomes are still being studied. Some patients experience sustained pain relief and improved joint function, while others may see more modest results. Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider is important to monitor the effectiveness of the therapy.
Stem cell therapy for arthritis is an evolving field with ongoing research. It's important to have detailed discussions with healthcare providers to understand the potential benefits, risks, and suitability of the treatment for your specific condition.
Top Doctors
Top Hospitals
STEM CELL TRANSPLANT FOR ARTHRITIS COST IN INDIA

Duration of Treatment
15 Days
Days of Stay
2 days in Hospital
Anesthesia
No Need
Cost
7000 to 12000 USD
Stem cell transplant for arthritis Cost in India
Stem cell transplant for arthritis is an emerging treatment aimed at repairing and regenerating damaged joint tissues, particularly cartilage, using stem cells. This therapy is considered especially for conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, where conventional treatments may not provide sufficient relief or halt disease progression.
What is Stem Cell Transplant in Arthritis?
Stem cell therapy for arthritis involves injecting stem cells into the affected joints to promote healing and regeneration of the damaged tissues. Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including cartilage, bone, and muscle cells, which makes them ideal for repairing joint damage.
Types of Stem Cells Used:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs):
- Derived from bone marrow, adipose (fat) tissue, or umbilical cord tissue.
- Known for their ability to differentiate into cartilage and bone cells.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs):
- Typically derived from bone marrow or peripheral blood.
- More commonly used in treatments for blood-related disorders but can also aid in tissue regeneration.
Benefits:
- Pain Reduction: Decreased inflammation and pain in the affected joints.
- Improved Function: Enhanced joint mobility and function.
- Tissue Regeneration: Potential regeneration of cartilage and other joint tissues.
- Reduced Need for Surgery: May delay or prevent the need for joint replacement surgery.
The cost of stem cell transplant therapy for arthritis in India can vary widely based on several factors, including the type of stem cells used, the healthcare facility, the city, and the specific treatment protocol. Here are some general estimates and factors that influence the cost:
General Stem cell transplant for arthritis Cost in India:
-
Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells:
- Cost: 15000 to 20000 USD per treatment session.
-
Adipose (Fat) Tissue-Derived Stem Cells:
- Cost: 7000 to 8000 USD per treatment session.
-
Umbilical Cord-Derived Stem Cells:
- Cost: 8500 to 15000 USD per treatment session.
Factors Influencing the Cost:
- Type of Stem Cells: Different sources of stem cells (bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord) have different extraction and processing costs.
- Healthcare Facility: Stem cell therapy in India Costs are generally higher in reputed private hospitals compared to smaller clinics or government hospitals.
- City: Metropolitan cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, and Chennai may have higher costs compared to smaller cities or towns.
- Treatment Protocol: The number of stem cell injections required, additional therapies, and follow-up care can influence the overall cost.
- Surgeon’s Expertise: Experienced and renowned specialists may charge higher fees.
- Preoperative and Postoperative Care: Includes consultation fees, diagnostic tests, medications, and follow-up visits.
Insurance Coverage:
- Many health insurance policies in India do not yet cover stem cell therapy as it is considered experimental or investigational. It is advisable to check with your insurance provider for specific coverage details.
Consultation and Diagnostic Tests:
- Initial consultation fees and diagnostic tests (such as MRI, X-rays, and blood tests) may cost between 5,000 to 15,000, depending on the hospital and location.
Additional Costs:
- Travel and Accommodation: For patients traveling from other cities or countries, travel and accommodation costs can add to the overall expense.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up visits to monitor progress and additional treatments, if necessary.
For the most accurate and personalized Stem cell transplant for arthritis Cost in India estimate, it’s best to contact specific hospitals or stem cell therapy centers directly. They can provide detailed information based on individual cases and requirements.
symptoms
Stem cell therapy for arthritis aims to alleviate symptoms and improve joint function by promoting the regeneration of damaged tissues. While stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, patients may experience various symptoms or side effects during and after the treatment. Here are some common symptoms and side effects associated with stem cell therapy for arthritis:
Common Symptoms and Side Effects:
- Injection Site Reactions:
- Pain and Discomfort: Mild to moderate pain or discomfort at the injection site.
- Swelling: Temporary swelling around the injection area.
- Redness and Bruising: Localized redness and bruising, which usually resolve within a few days.
- Systemic Reactions:
- Fever: Low-grade fever can occur as an immune response to the treatment.
- Fatigue: Temporary fatigue or tiredness following the procedure.
- Inflammation and Soreness:
- Joint Inflammation: Mild inflammation and soreness in the treated joint, which typically subside within a few days to a week.
- Allergic Reactions:
- Rare: Allergic reactions to the materials used in the procedure or the stem cells themselves are rare but possible.
- Infection:
- Risk: Although rare, there is a risk of infection at the injection site. Signs of infection include increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth, and fever.
Expected Improvements:
- Pain Relief:
- Reduced Joint Pain: Many patients experience a reduction in joint pain within weeks to months after the treatment.
- Improved Mobility:
- Enhanced Joint Function: Improved range of motion and joint function, allowing for better mobility and physical activity.
- Cartilage Regeneration:
- Tissue Repair: Stem cells can promote the regeneration of damaged cartilage and other joint tissues, leading to structural improvements in the joint.
- Reduced Inflammation:
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce chronic inflammation in the affected joints
risk factors
Risks and Considerations:
- Infection: Risk of infection at the injection site.
- Allergic Reaction: Possible allergic reactions to the injected materials.
- Variable Results: Efficacy can vary from patient to patient.
- Cost: Stem cell therapy can be expensive and is not always covered by insurance.
Current Status and Research:
- Clinical Trials: Ongoing research and clinical trials are exploring the effectiveness and safety of stem cell therapy for arthritis.
- Regulatory Approval: Stem cell therapies are still under investigation and may not be widely approved or available for arthritis treatment in all regions.
Consultation and Eligibility:
- Consultation: A detailed consultation with an orthopedic specialist or a rheumatologist is necessary to determine if a patient is a good candidate for stem cell therapy.
- Eligibility: Factors like the type and severity of arthritis, overall health, and previous treatments are considered.
Stem cell therapy for arthritis holds promise but is still an evolving field. It’s essential to have realistic expectations and to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare provider.
preparation
Preparation for stem cell therapy for arthritis involves several steps to ensure the patient is a suitable candidate and to optimize the chances of a successful outcome. Here are the key steps in the preparation process:
1. Consultation and Evaluation:
- Initial Consultation: Schedule an appointment with a specialized orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist experienced in stem cell therapy.
- Medical History: Provide a detailed medical history, including current medications, previous treatments, and any underlying health conditions.
- Physical Examination: Undergo a thorough physical examination to assess the severity of arthritis and overall joint function.
2. Diagnostic Tests:
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound may be conducted to evaluate the extent of joint damage and guide the treatment plan.
- Blood Tests: Routine blood tests to check for any underlying conditions that could affect the treatment.
- Joint Fluid Analysis: In some cases, a sample of joint fluid may be analyzed to rule out infections or other conditions.
3. Determining Candidacy:
- Eligibility: The doctor will determine if the patient is a suitable candidate for stem cell therapy based on the type and severity of arthritis, overall health, and previous treatments.
- Alternative Treatments: Discuss alternative treatment options and compare them with stem cell therapy to make an informed decision.
4. Pre-Treatment Instructions:
- Medications: Review and possibly adjust current medications. Patients may need to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or anti-inflammatory drugs, before the procedure.
- Supplements: Inform the doctor about any supplements being taken, as some may need to be discontinued prior to treatment.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to optimize overall health and the body’s response to the treatment.
procedure
5. Preparation for the Procedure:
- Fasting: Follow any fasting instructions provided by the doctor, especially if sedation or anesthesia will be used during the procedure.
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated in the days leading up to the procedure.
- Arrangements: Arrange for transportation to and from the medical facility, as patients may not be able to drive immediately after the procedure.
6. The Day of the Procedure:
- Arrival: Arrive at the medical facility as instructed, typically a few hours before the scheduled procedure.
- Consent: Sign any necessary consent forms after discussing the procedure, risks, and benefits with the healthcare provider.
- Comfort: Wear comfortable clothing and avoid wearing jewelry or accessories that may interfere with the procedure.
7. During the Procedure:
- Anesthesia: Depending on the type of stem cell therapy, local anesthesia, sedation, or general anesthesia may be used to ensure comfort during the procedure.
- Stem Cell Harvesting:
- Bone Marrow Aspiration: If bone marrow-derived stem cells are used, a needle is inserted into the pelvic bone to extract bone marrow.
- Adipose Tissue Extraction: If adipose (fat) tissue-derived stem cells are used, a small amount of fat is extracted from areas like the abdomen or thigh.
- Umbilical Cord Tissue: Pre-prepared stem cells from umbilical cord tissue are used without the need for harvesting from the patient.
- Stem Cell Processing: The harvested stem cells are processed and concentrated in a laboratory setting to prepare them for injection.
- Injection: The processed stem cells are injected directly into the affected joint(s) using imaging guidance (such as ultrasound) to ensure precise placement.
post procedure
8. Post-Procedure Care:
- Observation: Patients are typically observed for a short period after the procedure to monitor for any immediate reactions.
- Pain Management: Mild pain or discomfort at the injection site can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, as advised by the doctor.
- Activity Restrictions: Follow any activity restrictions or guidelines provided by the healthcare provider, such as avoiding strenuous activities for a few days.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Schedule and attend follow-up appointments to monitor progress and assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
9. Long-Term Care:
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can help improve joint function and enhance the benefits of stem cell therapy.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management, to support joint health and overall well-being.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor symptoms and report any changes or concerns to the healthcare provider to ensure timely interventions if needed.
By carefully following these preparation steps, patients can optimize their outcomes from stem cell therapy for arthritis and improve their chances of achieving pain relief and improved joint function.
success rate
The success of stem cell therapy for arthritis varies depending on several factors, including the type of arthritis, the severity of the condition, the source of stem cells used, and the individual patient's health. Here's a breakdown of what to consider regarding the success and outcomes of stem cell therapy for arthritis:
Factors Influencing Success:
- Type of Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): Stem cell therapy has shown promising results in treating osteoarthritis, especially in the knees and hips. Success rates can vary, but many patients report improved pain relief and joint function.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): The effectiveness of stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis is still under investigation. RA often requires more complex approaches due to its systemic nature and the presence of joint deformities.
- Severity of the Condition:
- Early-Stage Arthritis: Patients with early-stage arthritis or less severe joint damage often experience better outcomes compared to those with advanced or end-stage arthritis.
- Advanced Arthritis: Stem cell therapy may provide limited relief in cases of severe joint damage or where there is significant bone loss or deformity.
- Type of Stem Cells Used:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord tissue, MSCs are commonly used and have shown positive results in many clinical studies.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs): More commonly used for blood disorders, their role in arthritis is less established.
- Source of Stem Cells:
- Autologous Stem Cells: Using the patient’s own stem cells (from bone marrow or adipose tissue) generally has a lower risk of rejection and complications.
- Allogeneic Stem Cells: Stem cells from donors (e.g., umbilical cord tissue) may be effective but can involve additional considerations related to donor compatibility and processing.
- Individual Patient Factors:
- Overall Health: General health, including the presence of other medical conditions, can impact the success of the therapy.
- Compliance: Adherence to post-treatment care, including physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, plays a crucial role in achieving optimal outcomes.
Expected Outcomes:
- Pain Relief:
- Many patients experience a significant reduction in joint pain and discomfort after stem cell therapy. Pain relief can often begin within a few weeks and may continue to improve over several months.
- Improved Joint Function:
- Enhanced joint mobility and function are commonly reported. Patients often find it easier to perform daily activities and engage in physical exercise.
- Cartilage Regeneration:
- Stem cell therapy aims to regenerate damaged cartilage. While some studies show evidence of cartilage repair or regeneration, the extent of this repair can vary.
- Reduced Inflammation:
- Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties that can help decrease joint inflammation, contributing to overall symptom relief.
Clinical Research and Evidence:
- Clinical Trials: Ongoing research and clinical trials continue to evaluate the effectiveness of stem cell therapy for arthritis. Some studies have reported positive outcomes, while others highlight the need for further research to confirm long-term benefits and safety.
- Success Rates: Success rates can vary widely. Some studies report significant improvements in symptoms for a majority of patients, while others show more modest results.
Considerations and Limitations:
- Variable Results: Results can be inconsistent, with some patients experiencing significant benefits and others seeing minimal improvement.
- Long-Term Effects: The long-term effects of stem cell therapy are still being studied. Patients should discuss potential outcomes and risks with their healthcare provider.
- Cost and Accessibility: Stem cell therapy can be expensive and may not be covered by insurance. Patients should consider the financial implications and explore available options.
Consultation and Personalized Approach:
- Specialist Consultation: It is important to consult with a specialist experienced in stem cell therapy for arthritis to determine if the treatment is suitable and to discuss expected outcomes.
- Personalized Treatment Plan: Each patient’s treatment plan should be tailored to their specific condition, health status, and treatment goals.
Overall, while stem cell therapy for arthritis shows promise, it is essential to have realistic expectations and to work closely with healthcare providers to assess the potential benefits and risks based on individual circumstances.
faqs from doctor
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about stem cell therapy for arthritis:
1. What is stem cell therapy for arthritis?
Answer: Stem cell therapy for arthritis involves injecting stem cells into affected joints to promote tissue repair and regeneration. The goal is to reduce pain, improve joint function, and potentially regenerate damaged cartilage.
2. How does stem cell therapy work for arthritis?
Answer: Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including cartilage and bone cells. When injected into damaged joints, they can help repair and regenerate tissues, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain.
3. What types of stem cells are used in arthritis treatment?
Answer: Commonly used stem cells include:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Typically derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord tissue.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs): More commonly used for blood-related disorders, but may also have applications in arthritis.
4. Is stem cell therapy safe?
Answer: Stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, but it carries some risks, such as infection, allergic reactions, and pain at the injection site. It is important to discuss potential risks with a healthcare provider and choose a reputable facility.
5. How effective is stem cell therapy for arthritis?
Answer: The effectiveness of stem cell therapy varies. Many patients experience significant pain relief and improved joint function, especially in early-stage arthritis. However, results can be variable, and ongoing research is needed to confirm long-term benefits and safety.
6. How long does it take to see results from stem cell therapy?
Answer: Patients may begin to notice improvements in pain and joint function within a few weeks to months after the procedure. Full benefits may take several months to become evident.
7. How is the stem cell therapy procedure performed?
Answer: The procedure typically involves:
- Harvesting: Stem cells are collected from the patient’s bone marrow, adipose tissue, or obtained from a donor source.
- Processing: The collected stem cells are processed and concentrated.
- Injection: The processed stem cells are injected into the affected joint using imaging guidance to ensure precise placement.
8. What are the potential side effects of stem cell therapy?
Answer: Common side effects include mild pain or discomfort at the injection site, swelling, and redness. Rare but possible side effects include infection and allergic reactions. Patients should monitor for any unusual symptoms and report them to their healthcare provider.
9. How should I prepare for stem cell therapy?
Answer: Preparation may include:
- Medical Evaluation: Undergoing a thorough medical evaluation and diagnostic tests.
- Medication Review: Discussing current medications with your doctor and possibly adjusting them.
- Pre-Procedure Instructions: Following fasting or other pre-procedure instructions as advised by your healthcare provider.
10. What is the cost of stem cell therapy for arthritis?
Answer: The cost varies widely depending on factors such as the type of stem cells used, the healthcare facility, and the city. On average, the cost ranges from ?1,50,000 to ?7,00,000 per treatment session. It is advisable to check with specific hospitals or clinics for accurate pricing.
11. Is stem cell therapy covered by insurance?
Answer: Many insurance policies do not cover stem cell therapy as it is often considered experimental or investigational. Patients should check with their insurance provider for coverage details and explore financing options if needed.
12. How many sessions of stem cell therapy will I need?
Answer: The number of sessions required can vary based on the individual’s condition and response to treatment. Some patients may benefit from a single session, while others may require multiple sessions.
13. What should I expect after the procedure?
Answer: After the procedure, you may experience mild pain or swelling at the injection site. It is important to follow post-procedure care instructions, including activity restrictions and follow-up appointments, to monitor progress and ensure optimal outcomes.
14. How do I choose a facility for stem cell therapy?
Answer: Choose a reputable facility with experienced specialists in stem cell therapy. Look for accreditation, review patient testimonials, and consult with the healthcare provider to ensure the facility meets your needs and expectations.
15. What are the long-term outcomes of stem cell therapy for arthritis?
Answer: Long-term outcomes are still being studied. Some patients experience sustained pain relief and improved joint function, while others may see more modest results. Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider is important to monitor the effectiveness of the therapy.
Stem cell therapy for arthritis is an evolving field with ongoing research. It's important to have detailed discussions with healthcare providers to understand the potential benefits, risks, and suitability of the treatment for your specific condition.




















