Duration of Treatment
depending on condition
Days of Stay
OPD basis
Anesthesia
not required
Cost
On Request
What is Glomerulonephritis?
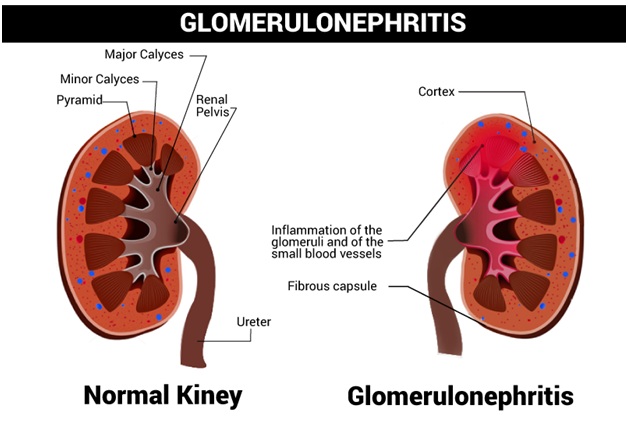
A glomerulonephritis is a group of diseases that damage to the tiny filters inside your kidneys (the glomeruli). If your glomeruli are damaged, your kidneys will stop working properly, and you can go into kidney failure.
There different types of glomerulonephritis?
- Acute
- Chronic.
Glomerulonephritis signs include:
- Rashes
- Joint pain
- Breathing problems
- Tiredness
- High blood pressure.
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Nosebleeds
- weight loss
- Urinating less often
- Blood in your urine
Risk factors for glomerulonephritis include:
- Viral infections (such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C ).
- Acute glomerulonephritis may develop into chronic.
- Long-term, glomerulonephritis.
- Damage to kidneys from hypertension.
To identify the diagnosis doctor advised to go for complete evolution - usually, blood investigation, 24 hours urine test and routine test, ultrasound, (CT) scans or magnetic resonance (MRI) imaging and Kidney biopsy.
Treatment for glomerulonephritis depends on the cause of patient condition and symptoms. There is no specific treatment for the chronic glomerulonephritis; nephrologist will advise some line of treatment to the patient:
Therapies for associated kidney failure
In acute glomerulonephritis and acute kidney failure, dialysis can help remove excess fluid and control high blood pressure. The only long-term therapies for end-stage kidney disease are kidney dialysis and kidney transplant.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause of glomerulonephritis. For example, control of blood pressure and blood sugar with medications would be important in the treatment glomerulonephritis related to hypertension and diabetes. In addition, the following steps may be taken to aid kidney function or reduce further damage:
Medications
The patient may need to take medicines to maintain the lower blood pressure, help reduce the amount of protein that leaks into your urine and medications to suppress the immune system such as:
- angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
- angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB)
Lifestyle Changes
- Restrict salt and water intake
- Control Blood pressure
- Restrict intake of potassium, phosphorous, and magnesium
- Cut down on protein in the diet
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise
- Take calcium supplements
Dialysis and Transplant
In severe cases that can't be improved with other treatments, or kidneys are unable to remove sufficient wastes from the blood than dialysis or Kidney Transplant require.
Plasma exchange
Plasma exchange involves removing some of the plasma from your blood, usually, if the patient has a type of glomerulonephritis called ANCA vasculitis or anti-glomerular basement membrane disease.
Vaccinations
Patient with glomerulonephritis gets easily infections so it’s advisable to protect infection by having vaccination of seasonal flu and a pneumonia jab.
- The doctor will give complete information about post care of glomerulonephritis, regarding recovery; taking medications and managing lifestyle.
- Patients are advised Kidney transplant
The success rate depends on the patient depends upon the patient condition and symptoms, finally, a kidney transplant is the only option in acute cases.
- Are you board-certified Nephrologist doctor?
- How many years’ experience of you has in this field?
- How badly do my kidneys seem to be affected?
- What tests do I need?
- Is my condition likely temporary or chronic?
- Do I need dialysis?
- What restrictions do I need to follow?
- Why does glomerulonephritis have proteinuria?
- What is the diet for glomerulonephritis?
- Is glomerulonephritis fatal?
- How do you know if you have kidney disease?
- Is there a cure for Bright's disease?
- Is glomerulonephritis an autoimmune disease?
Top Doctors
Top Hospitals
GLOMERULONEPHRITIS TREATMENT

Duration of Treatment
depending on condition
Days of Stay
OPD basis
Anesthesia
not required
Cost
On Request
What is Glomerulonephritis?
A glomerulonephritis is a group of diseases that damage to the tiny filters inside your kidneys (the glomeruli). If your glomeruli are damaged, your kidneys will stop working properly, and you can go into kidney failure.
There different types of glomerulonephritis?
- Acute
- Chronic.
symptoms
Glomerulonephritis signs include:
- Rashes
- Joint pain
- Breathing problems
- Tiredness
- High blood pressure.
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Nosebleeds
- weight loss
- Urinating less often
- Blood in your urine
risk factors
Risk factors for glomerulonephritis include:
- Viral infections (such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C ).
- Acute glomerulonephritis may develop into chronic.
- Long-term, glomerulonephritis.
- Damage to kidneys from hypertension.
preparation
To identify the diagnosis doctor advised to go for complete evolution - usually, blood investigation, 24 hours urine test and routine test, ultrasound, (CT) scans or magnetic resonance (MRI) imaging and Kidney biopsy.
procedure
Treatment for glomerulonephritis depends on the cause of patient condition and symptoms. There is no specific treatment for the chronic glomerulonephritis; nephrologist will advise some line of treatment to the patient:
Therapies for associated kidney failure
In acute glomerulonephritis and acute kidney failure, dialysis can help remove excess fluid and control high blood pressure. The only long-term therapies for end-stage kidney disease are kidney dialysis and kidney transplant.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause of glomerulonephritis. For example, control of blood pressure and blood sugar with medications would be important in the treatment glomerulonephritis related to hypertension and diabetes. In addition, the following steps may be taken to aid kidney function or reduce further damage:
Medications
The patient may need to take medicines to maintain the lower blood pressure, help reduce the amount of protein that leaks into your urine and medications to suppress the immune system such as:
- angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
- angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB)
Lifestyle Changes
- Restrict salt and water intake
- Control Blood pressure
- Restrict intake of potassium, phosphorous, and magnesium
- Cut down on protein in the diet
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise
- Take calcium supplements
Dialysis and Transplant
In severe cases that can't be improved with other treatments, or kidneys are unable to remove sufficient wastes from the blood than dialysis or Kidney Transplant require.
Plasma exchange
Plasma exchange involves removing some of the plasma from your blood, usually, if the patient has a type of glomerulonephritis called ANCA vasculitis or anti-glomerular basement membrane disease.
Vaccinations
Patient with glomerulonephritis gets easily infections so it’s advisable to protect infection by having vaccination of seasonal flu and a pneumonia jab.
post procedure
- The doctor will give complete information about post care of glomerulonephritis, regarding recovery; taking medications and managing lifestyle.
- Patients are advised Kidney transplant
success rate
The success rate depends on the patient depends upon the patient condition and symptoms, finally, a kidney transplant is the only option in acute cases.
faqs from doctor
- Are you board-certified Nephrologist doctor?
- How many years’ experience of you has in this field?
- How badly do my kidneys seem to be affected?
- What tests do I need?
- Is my condition likely temporary or chronic?
- Do I need dialysis?
- What restrictions do I need to follow?
- Why does glomerulonephritis have proteinuria?
- What is the diet for glomerulonephritis?
- Is glomerulonephritis fatal?
- How do you know if you have kidney disease?
- Is there a cure for Bright's disease?
- Is glomerulonephritis an autoimmune disease?





























