Duration of Treatment
5 to 7 hours
Days of Stay
5 to 10 Days
Anesthesia
as per advised
Cost
15000 t0 35000 USD
How Much Does Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery Cost in India?
Are you looking for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery Cost in India at one of the best hospitals at an affordable cost"? Here, we answer the question and explain how to choose the top Cardiac surgeon for better results. To make an appointment, call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782
We have shortlisted the list of the top cardiac Hospitals and Surgeons based on Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of surgeons, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery Cost in India: starting from 15000 to 35000 USD.
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD (as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day)
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day).
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will plan after the fresh evaluation reports.
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery Cost in India can vary as per the diagnosis, patient's conditions, surgeon experience, Implant quality, hospital facilities, and city.
- To make an appointment, learn more about the treatment, read the below information, or call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782. Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
The Top 10 Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgeons in India:
- Dr. Naresh Trehan
- Dr. Ramakanta Panda
- Dr. Devi Prasad Shetty
- Dr. S. K. Sinha
- Dr. Yugal K. Mishra
- Dr. Rajesh Sharma
- Dr. K. R. Balakrishnan
- Dr. Ashok Seth
- Dr. C. P. S. Chauhan
- Dr. Sandeep Attawar
Which is the Best Hospital for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery in India?
- MANIPAL HOSPITAL
- BLK HOSPITAL
- MAX HOSPITAL
- JAYPEE HOSPITAL
- APOLLO HOSPITAL
- FORTIS ESCORT HOSPITAL
- GLOBAL HOSPITAL
- HCG CANCER HOSPITAL
- ARTEMIS HOSPITAL
- MEDANTA HOSPITAL
- ASTER HOSPITAL
- YASHODHA HOSPITAL
- GLOBAL HOSPITAL
- NARAYANA HOSPITAL
Why you choose Peace Medical Tourism?
We are one of the best health care services providers for more than 10 years of experience to provide the best treatment at an affordable cost and guide our international patients to choose the top destination as per patient's budget and treatment.
- Comprehensive and 100% transparency.
- Help to Choose the Best Option for Cancer Treatment.
- Very highly skilled surgeon in India team.
- World-class technology for surgery.
- The high success rate of procedures with international standards.
- Affordable Cost of surgery.
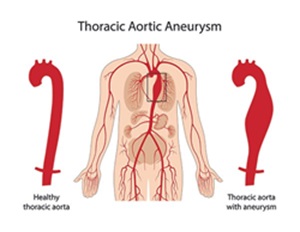
What is a Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm?
A thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) is a bulging or dilation in the wall of the thoracic aorta, the part of the aorta that runs through the chest. The aorta is the largest artery in the body, responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. When the wall of the aorta weakens, it can balloon outward, forming an aneurysm. If left untreated, a thoracic aortic aneurysm can rupture, leading to life-threatening internal bleeding.
Types of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms
Thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) can be classified based on their location, shape, and underlying cause. Understanding the different types helps in determining the appropriate treatment approach and management strategy. Here’s a detailed look at the various types of thoracic aortic aneurysms:
Based on Location
-
Ascending Aortic Aneurysm
- Location: Occurs in the ascending aorta, the section of the aorta that rises from the heart’s left ventricle.
- Common Causes: Marfan syndrome, bicuspid aortic valve, and other genetic conditions.
- Risks: High risk of rupture and aortic dissection.
-
Aortic Arch Aneurysm
- Location: Found in the aortic arch, the curved portion of the aorta that gives rise to branches supplying blood to the head, neck, and arms.
- Common Causes: Atherosclerosis, trauma, and congenital conditions.
- Risks: Can affect blood flow to the brain and upper body, leading to complications like stroke.
-
Descending Aortic Aneurysm
- Location: Located in the descending thoracic aorta, which extends downward from the aortic arch through the chest.
- Common Causes: Atherosclerosis, hypertension, and trauma.
- Risks: May extend into the abdominal aorta, potentially causing abdominal aortic aneurysms.
Based on Shape
-
Fusiform Aneurysm
- Shape: Uniform, spindle-shaped dilation that involves the entire circumference of the aortic wall.
- Characteristics: Commonly found in the descending aorta.
- Risks: Generally grow slowly but can still rupture if they become too large.
-
Saccular Aneurysm
- Shape: Localized, balloon-like outpouching on one side of the aorta.
- Characteristics: More prone to rupture compared to fusiform aneurysms due to their asymmetrical shape.
- Risks: Often associated with trauma, infections, or certain genetic conditions.
Based on Underlying Cause
-
Genetic and Congenital Aneurysms
- Causes: Conditions like Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, and bicuspid aortic valve.
- Characteristics: These aneurysms typically develop at a younger age and may be associated with other connective tissue disorders.
- Risks: High risk of rapid growth and rupture.
-
Degenerative Aneurysms
- Causes: Age-related degeneration of the aortic wall, often due to atherosclerosis and hypertension.
- Characteristics: More common in older adults.
- Risks: Gradual enlargement with potential for rupture if untreated.
-
Traumatic Aneurysms
- Causes: Result from injury to the chest, such as from a car accident or fall.
- Characteristics: Can occur at any point in the thoracic aorta.
- Risks: May develop quickly and require immediate medical attention.
-
Infectious (Mycotic) Aneurysms
- Causes: Infections that weaken the aortic wall, such as bacterial endocarditis or syphilis.
- Characteristics: Often saccular and located in the descending aorta.
- Risks: High risk of rupture and need for prompt treatment with antibiotics and possibly surgery.
-
Inflammatory Aneurysms
- Causes: Chronic inflammatory conditions like Takayasu arteritis or giant cell arteritis.
- Characteristics: Inflammation causes thickening and weakening of the aortic wall.
- Risks: Can lead to rapid growth and rupture if inflammation is not controlled.
Additional Considerations
-
Pseudoaneurysms (False Aneurysms)
- Causes: Result from a tear in the aortic wall leading to a contained rupture. Unlike true aneurysms, which involve all three layers of the aortic wall, pseudoaneurysms are contained by the outer layers or surrounding tissues.
- Characteristics: Often occur due to trauma or surgical complications.
- Risks: High risk of rupture and require urgent treatment.
-
Dissecting Aneurysms
- Causes: Aortic dissection, where a tear in the inner layer of the aorta causes blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, leading to the formation of a false lumen.
- Characteristics: Can occur anywhere in the aorta and are classified based on the location and extent of the dissection.
- Risks: Highly dangerous and can lead to aortic rupture, organ damage, and death if not treated promptly.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Early diagnosis and regular monitoring are crucial for managing thoracic aortic aneurysms. Diagnostic tools include:
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart and aorta.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the aorta.
- MRI: Offers detailed images without radiation exposure.
- Angiography: Involves injecting a contrast dye into the bloodstream to visualize the aorta.
Symptoms forThoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
TAAs often grow slowly and might not cause symptoms until they are large or ruptured. Symptoms, when present, may include:
-
Chest or back pain
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing or hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
Risk Factors of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery, whether it is open surgery or endovascular repair, carries significant risks due to the complexity of the procedure and the critical nature of the aorta. Understanding these risks is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions and prepare adequately for the surgery. Below are the key risk factors associated with thoracic aortic aneurysm surgery:
General Surgical Risks
-
Bleeding
- Excessive bleeding during or after surgery is a common risk, especially given the large blood vessels involved.
-
Infection
- Risk of infection at the incision site or within the chest cavity.
-
Reactions to Anesthesia
- Allergic reactions or complications arising from general anesthesia.
-
Blood Clots
- Formation of blood clots that can lead to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism.
Specific Risks Related to TAA Surgery
-
Aortic Dissection
- A tear in the aorta's inner layer can occur, leading to a life-threatening condition where blood flows between the layers of the aorta wall.
-
Rupture of the Aneurysm
- During the procedure, there is a risk of the aneurysm rupturing, which can cause severe internal bleeding.
-
Graft Leakage or Failure
- The synthetic graft used to replace the aneurysmal section of the aorta may leak or fail, leading to complications.
-
Stroke
- A stroke can occur if blood flow to the brain is disrupted during the surgery.
-
Spinal Cord Injury
- Risk of spinal cord injury due to decreased blood supply, potentially resulting in paralysis or other neurological deficits.
-
Heart Attack
- The stress of surgery can precipitate a heart attack, particularly in patients with existing heart conditions.
Risk Factors Related to Patient Health
-
Age
- Older patients generally face higher surgical risks due to decreased physiological resilience.
-
Pre-existing Conditions
- Conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) increase surgical risks.
-
Previous Cardiac Surgeries
- Patients with a history of cardiac surgeries have increased risks due to scar tissue and previous alterations in anatomy.
-
Genetic Conditions
- Conditions like Marfan syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which affect connective tissue, can complicate surgery.
Technical and Procedure-Related Risks
-
Complex Anatomy
- Variations in the anatomy of the aorta or surrounding structures can increase the difficulty of the surgery.
-
Duration of Surgery
- Longer surgical times are associated with higher risks of complications such as infection, bleeding, and organ dysfunction.
-
Experience of the Surgical Team
- The skill and experience of the surgical team play a critical role in minimizing risks.
Post-Surgical Risks
-
Respiratory Complications
- Risk of pneumonia or other respiratory issues due to prolonged immobility or the effects of anesthesia.
-
Kidney Dysfunction
- Potential for acute kidney injury due to decreased blood flow or use of contrast dyes during imaging procedures.
-
Delayed Healing
- Factors such as poor nutrition, diabetes, or smoking can delay wound healing and increase the risk of infection.
-
Recurrent Aneurysms
- There is a risk that new aneurysms may develop in other sections of the aorta, necessitating further monitoring and potential future surgeries.
Preparation for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
Preparing for thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery involves multiple steps to ensure the patient's safety and improve the chances of a successful outcome. The preparation process includes a thorough medical evaluation, optimization of health conditions, and psychological readiness. Here’s a detailed guide on how to prepare for TAA surgery:
Medical Evaluation and Diagnostics
-
Comprehensive Medical History
- Review of personal and family medical history.
- Assessment of symptoms and risk factors.
-
Physical Examination
- Detailed physical examination focusing on cardiovascular health.
-
Imaging Studies
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the aorta to assess the size and location of the aneurysm.
- MRI: Offers detailed imaging without radiation exposure.
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to create images of the heart and aorta.
- Angiography: Involves injecting contrast dye to visualize the aorta and identify the aneurysm.
-
Laboratory Tests
- Blood tests to assess overall health, including kidney function, liver function, and blood clotting ability.
- Urine tests to check for kidney function and other underlying conditions.
-
Cardiovascular Assessment
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the electrical activity of the heart.
- Stress Test: Evaluates how the heart performs under physical stress.
- Cardiac Catheterization: Examines the coronary arteries for any blockages.
Optimizing Health Conditions
-
Blood Pressure Control
- Manage hypertension with medications and lifestyle changes to reduce stress on the aorta.
-
Blood Sugar Management
- Control diabetes through diet, medication, and monitoring blood sugar levels.
-
Smoking Cessation
- Quit smoking to improve lung function and blood circulation.
-
Nutritional Optimization
- Maintain a balanced diet to ensure adequate nutrition for healing.
- Consider supplements if necessary, as advised by a healthcare provider.
-
Weight Management
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of complications.
-
Medications
- Adjust or stop certain medications as directed by the surgeon.
- Start any new medications prescribed to optimize health before surgery.
Psychological and Emotional Preparation
-
Patient Education
- Understand the nature of the surgery, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
- Discuss the procedure, recovery process, and long-term care with the surgical team.
-
Support System
- Arrange for family or friends to provide support during the hospital stay and recovery period.
- Consider counseling or support groups for emotional support.
-
Preoperative Instructions
- Follow specific instructions provided by the surgical team, including fasting guidelines and medication adjustments.
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Cost in India
Hospital and Surgical Preparation
-
Preoperative Appointment
- Attend a preoperative appointment for final assessments and to address any questions or concerns.
-
Consent Form
- Sign informed consent forms after discussing the surgery with the healthcare team.
-
Packing for the Hospital
- Pack necessary items for the hospital stay, including comfortable clothing, personal hygiene items, and any prescribed medications.
-
Transportation Arrangements
- Arrange for transportation to and from the hospital.
-
Advance Directives
- Prepare advance directives, such as a living will or durable power of attorney for healthcare, if desired.
Day Before Surgery
-
Fasting
- Follow fasting instructions, typically no food or drink after midnight before the surgery.
-
Medication
- Take any prescribed medications as directed, with a small sip of water if allowed.
-
Hygiene
- Bathe or shower using antibacterial soap to reduce the risk of infection.
-
Rest
- Get a good night’s sleep to ensure the body is well-rested for surgery.
Day of Surgery
-
Arrival at the Hospital
- Arrive at the hospital on time as instructed.
- Check-in and complete any remaining paperwork.
-
Preoperative Area
- Change into a hospital gown and prepare for surgery.
- Meet with the surgical team, including the anesthesiologist, to review the procedure.
-
Intravenous (IV) Line
- An IV line will be placed to administer medications and fluids.
-
Final Checks
- Final health checks and discussions with the surgical team.
Procedures for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery involves various procedures tailored to the aneurysm's location, size, and the patient's overall health. The primary surgical procedures include open surgical repair and endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). Each procedure has its specific indications, steps, and recovery processes.
1. Open Surgical Repair
Indications:
- Large aneurysms (>5.5 cm in diameter) or rapidly growing aneurysms.
- Symptomatic aneurysms.
- Aneurysms with a high risk of rupture.
Procedure:
-
Anesthesia and Incision:
- The patient is placed under general anesthesia.
- An incision is made in the chest. The location of the incision (sternotomy or thoracotomy) depends on the aneurysm's position.
-
Exposure and Clamping:
- The aorta is exposed by carefully retracting tissues.
- Blood flow through the aorta is temporarily stopped using clamps placed above and below the aneurysm.
-
Aneurysm Resection:
- The aneurysmal section of the aorta is removed.
- The area is prepared for graft placement.
-
Graft Placement:
- A synthetic graft, usually made of Dacron or PTFE, is sewn into place to replace the removed section of the aorta.
- The clamps are slowly removed to restore blood flow through the graft.
-
Closure:
- The chest is closed in layers, and the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU) for monitoring.
Recovery:
- Initial recovery in the ICU for close monitoring.
- Pain management, respiratory therapy, and gradual mobilization.
- Hospital stay of about 7-10 days, with full recovery taking several weeks to months.
2. Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR)
Indications:
- Suitable for patients with anatomically favorable aneurysms.
- Patients at high risk for open surgery due to other medical conditions.
Procedure:
-
Anesthesia:
- The patient is usually placed under general anesthesia, though some cases may use regional anesthesia.
-
Access:
- Small incisions are made in the groin to access the femoral arteries.
-
Catheter Insertion:
- Catheters and guidewires are inserted through the femoral arteries and guided to the site of the aneurysm using fluoroscopic imaging.
-
Stent-Graft Deployment:
- A stent-graft is delivered via the catheter to the site of the aneurysm.
- The stent-graft is deployed and expanded to reinforce the aortic wall and exclude the aneurysm from blood flow.
-
Sealing and Verification:
- The stent-graft is positioned to ensure a tight seal above and below the aneurysm.
- Imaging is used to verify proper placement and seal.
-
Closure:
- The femoral artery incisions are closed, and the patient is monitored for any immediate complications.
Recovery:
- Shorter ICU stay compared to open surgery.
- Hospital discharge typically within 2-3 days.
- Faster overall recovery, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few weeks.
3. Hybrid Procedures
Indications:
- Complex aneurysms that involve multiple sections of the aorta.
- Patients with a combination of thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysms.
Procedure:
-
Combination of Open and Endovascular Techniques:
- Involves initial open surgical exposure followed by endovascular stent-graft placement.
-
Sequential Approach:
- May require staged procedures to address different sections of the aorta.
Recovery:
- Depends on the extent and combination of procedures performed.
- Typically involves longer recovery compared to EVAR but shorter than extensive open repairs.
4. Adjunct Procedures
-
Valve-Sparing Aortic Root Replacement (David Procedure):
- Indicated for aneurysms involving the aortic root.
- Preserves the patient’s native aortic valve while replacing the aneurysmal aortic root with a graft.
-
Bentall Procedure:
- Indicated for aneurysms involving the aortic root and valve.
- Involves replacement of the aortic valve, aortic root, and ascending aorta with a composite graft.
-
Frozen Elephant Trunk Procedure:
- Combines open surgical and endovascular techniques to treat extensive aneurysms involving the aortic arch and descending aorta.
- Uses a hybrid graft that is partially sewn in place and partially deployed endovascularly.
Preoperative and Postoperative Care
Preoperative:
- Comprehensive medical evaluation, including imaging studies.
- Optimization of medical conditions (e.g., controlling blood pressure, managing diabetes).
- Patient education and consent.
- Psychological support and preparation.
Postoperative:
- Intensive monitoring in the ICU for hemodynamic stability and complications.
- Pain management and respiratory therapy.
- Gradual mobilization and physical therapy.
- Regular follow-up with imaging to monitor graft integrity and aortic health.
Conclusion
Thoracic aortic aneurysm surgery includes various procedures, each tailored to the patient's specific condition and the aneurysm's characteristics. Open surgical repair, endovascular aneurysm repair, hybrid procedures, and adjunct techniques all play roles in managing TAAs. Comprehensive preoperative preparation, meticulous surgical execution, and diligent postoperative care are crucial for successful outcomes.
Postoperative Management for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
Postoperative management for thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery is crucial to ensure successful recovery, minimize complications, and promote long-term health. This involves a multi-disciplinary approach with careful monitoring, medication management, physical therapy, and patient education. Below are the key aspects of postoperative management:
Immediate Postoperative Care
-
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Monitoring
- Hemodynamic Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen levels, and central venous pressure.
- Ventilation Support: Mechanical ventilation may be required initially to support breathing.
- Pain Management: Administration of pain relief medications through intravenous (IV) lines or patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pumps.
-
Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
- IV Fluids: Carefully monitored to maintain hydration and electrolyte balance.
- Urine Output: Monitored closely to ensure adequate kidney function.
-
Blood Management
- Transfusions: Blood or blood products may be given if needed to manage anemia or blood loss.
- Anticoagulation: Use of anticoagulants may be started to prevent blood clots, as per the surgical team's recommendations.
-
Respiratory Care
- Incentive Spirometry: Encouraged to prevent atelectasis and promote lung expansion.
- Chest Physiotherapy: To aid in clearing secretions and improve respiratory function.
-
Cardiac Monitoring
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Continuous ECG monitoring to detect any cardiac arrhythmias.
- Echocardiogram: Performed as needed to assess heart function post-surgery.
Intermediate Postoperative Care
-
Transition from ICU to Step-Down Unit
- Stabilization: Once stable, patients are transferred from the ICU to a step-down unit for continued monitoring.
- Gradual Mobilization: Initiation of gentle physical activity, such as sitting up in bed and short walks, to prevent complications from immobility.
-
Pain Management
- Oral Medications: Transition from IV pain medications to oral pain relief as the patient becomes more stable.
- Pain Assessment: Regular assessment of pain levels and adjustment of medications as needed.
-
Nutritional Support
- Diet Advancement: Gradual progression from liquids to a regular diet as tolerated.
- Nutritional Monitoring: Ensuring adequate caloric and protein intake to promote healing.
-
Wound Care
- Incision Care: Regular inspection and care of the surgical incision to prevent infection.
- Drain Management: Monitoring and removal of any surgical drains.
-
Physical Therapy
- Rehabilitation Exercises: Physical therapy sessions to improve strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular fitness.
- Breathing Exercises: Continued emphasis on respiratory exercises to improve lung function.
Long-Term Postoperative Care
-
Follow-Up Appointments
- Regular Check-Ups: Scheduled visits with the surgeon and cardiologist to monitor recovery and detect any complications early.
- Imaging Studies: Follow-up imaging (e.g., CT scans, MRIs) to monitor the repair site and ensure there are no new aneurysms or complications.
-
Medication Management
- Antihypertensives: Medications to control blood pressure and reduce stress on the aorta.
- Statins: To manage cholesterol levels and reduce cardiovascular risk.
- Anticoagulants/Antiplatelets: As prescribed to prevent blood clots.
-
Lifestyle Modifications
- Diet: A heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity tailored to the patient’s condition, avoiding strenuous activities that can increase blood pressure.
- Smoking Cessation: Strong emphasis on quitting smoking to promote vascular health.
-
Monitoring for Complications
- Aortic Dissection/Rupture: Being vigilant for symptoms such as sudden severe chest or back pain.
- Graft Complications: Monitoring for signs of graft infection, leakage, or failure.
- Kidney Function: Regular blood tests to monitor kidney function, especially if contrast agents were used during the procedure.
-
Emotional and Psychological Support
- Counseling: Psychological support or counseling to help cope with the stress and anxiety associated with major surgery.
- Support Groups: Participation in support groups for patients with similar conditions to share experiences and encouragement.
Emergency Signs to Watch For
- Severe Chest Pain: Sudden, intense pain in the chest, back, or abdomen.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing.
- Neurological Symptoms: Sudden weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking.
- Swelling or Redness: At the incision site, indicating potential infection
Success Rate of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
The success rate of thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery varies based on several factors, including the type of surgery (open or endovascular), the patient’s overall health, the aneurysm’s size and location, and the experience of the surgical team. Generally, both open surgical repair and endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) have high success rates, but each comes with its own risks and benefits.
Open Surgical Repair Success Rates
-
General Success Rate:
- Open surgical repair of TAA typically has a success rate ranging from 90% to 95% in centers of excellence with experienced surgical teams.
-
Factors Influencing Success:
- Patient Age and Health: Younger patients with fewer comorbidities tend to have better outcomes.
- Aneurysm Size and Location: Smaller aneurysms and those located in less complex anatomical regions generally have higher success rates.
- Surgical Experience: Surgeons and centers with more experience in performing open TAA repairs tend to have better success rates and fewer complications.
-
Long-Term Outcomes:
- Patients typically enjoy a good quality of life post-surgery, with a low incidence of aneurysm recurrence in the repaired segment.
- Regular follow-ups and imaging are essential to monitor for any potential complications or new aneurysm formations.
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) Success Rates
-
General Success Rate:
- EVAR for TAA has a success rate of approximately 95% to 98%, making it slightly higher than open surgery due to its less invasive nature and lower immediate risk profile.
-
Factors Influencing Success:
- Anatomical Suitability: Patients whose aneurysms are anatomically suitable for EVAR tend to have higher success rates.
- Patient Health: Better overall health and fewer comorbid conditions improve outcomes.
- Technological Advancements: Advances in stent-graft technology and imaging techniques have improved the success rates of EVAR procedures.
-
Long-Term Outcomes:
- EVAR patients generally have quicker recoveries and shorter hospital stays compared to open surgery.
- Long-term follow-up is crucial to monitor the integrity of the stent-graft and ensure there are no endoleaks or other complications.
Comparative Success Rates and Considerations
-
Perioperative Mortality:
- Open Surgery: The perioperative mortality rate (death within 30 days of surgery) ranges from 5% to 10%.
- EVAR: The perioperative mortality rate is lower, typically around 1% to 5%.
-
Complication Rates:
- Open Surgery: Higher risk of complications such as bleeding, infection, and prolonged recovery time.
- EVAR: Lower immediate complication rates, but long-term monitoring for stent-graft complications is essential.
-
Hospital Stay and Recovery:
- Open Surgery: Longer hospital stays (7-10 days) and recovery periods (several weeks to months).
- EVAR: Shorter hospital stays (2-3 days) and quicker recovery (a few weeks).
-
Reintervention Rates:
- Open Surgery: Lower reintervention rates due to the durable nature of the surgical repair.
- EVAR: Higher reintervention rates due to potential issues with the stent-graft, such as migration or endoleaks.
Conclusion
Both open surgical repair and endovascular aneurysm repair for thoracic aortic aneurysms have high success rates, typically ranging from 90% to 98%. The choice between the two depends on various factors, including the patient’s health, the aneurysm’s characteristics, and the expertise of the surgical team. Open surgery offers long-term durability but comes with higher immediate risks and longer recovery, while EVAR provides a less invasive option with quicker recovery but requires ongoing monitoring for potential complications. The success of either procedure is enhanced by careful patient selection, thorough preoperative planning, and diligent postoperative care.
FAQs for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm in India
1. What is a thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA)?
A thoracic aortic aneurysm is an abnormal bulging or ballooning in the wall of the thoracic aorta, the major artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. It can lead to serious complications if it ruptures or dissects.
2. What causes a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
The primary causes include:
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
- Genetic conditions (e.g., Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome)
- High blood pressure
- Trauma or injury to the chest
- Infections affecting the aorta
3. What are the symptoms of a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
Many TAAs are asymptomatic, but symptoms can include:
- Chest pain or back pain
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing or hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
4. How is a thoracic aortic aneurysm diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical examination
- Imaging tests such as a chest X-ray, CT scan, MRI, or echocardiogram
- Angiography to visualize the aorta
5. What are the treatment options for a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
Treatment options depend on the size and growth rate of the aneurysm and the patient's overall health:
- Monitoring: Small, asymptomatic aneurysms may be monitored with regular imaging tests.
- Medication: To control blood pressure and reduce the risk of aneurysm growth.
- Surgery: Options include open surgical repair and endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR).
6. What is open surgical repair?
Open surgical repair involves removing the aneurysmal section of the aorta and replacing it with a synthetic graft. This procedure is more invasive and requires a longer recovery period.
7. What is endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR)?
EVAR is a minimally invasive procedure where a stent-graft is inserted into the aorta via small incisions in the groin. The stent-graft reinforces the aortic wall and prevents the aneurysm from rupturing.
8. What are the risks associated with TAA surgery?
Risks include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Heart attack or stroke
- Graft complications (e.g., leakage, migration)
- Kidney damage
9. What is the recovery time after TAA surgery?
- Open Surgery: Hospital stay of 7-10 days with a full recovery period of several weeks to months.
- EVAR: Shorter hospital stay of 2-3 days with a recovery period of a few weeks.
10. How often should I follow up after TAA surgery?
Regular follow-ups are crucial. Patients typically need imaging tests every 6-12 months to monitor the repair and detect any potential complications early.
11. What lifestyle changes are recommended after TAA surgery?
- Diet: Adopt a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Exercise: Engage in regular, moderate exercise while avoiding strenuous activities.
- Smoking Cessation: Quit smoking to improve vascular health.
- Blood Pressure Management: Keep blood pressure under control with medication and lifestyle changes.
12. What is the cost of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm in India?
The cost can vary significantly depending on the hospital, surgeon, and specific procedure:
- Open Surgery: Typically ranges from 15000 to 30000 USD.
- EVAR: Generally ranges from 10,000 to 15000 USD.
13. Are there specialized centers for TAA treatment in India?
Yes, several hospitals in India are renowned for TAA treatment, including:
- Jaypee Hospital New Delhi
- Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, New Delhi
- Medanta - The Medicity, Gurgaon
- Apollo Hospitals, Chennai
- Narayana Health, Bangalore
- Max Hospital
- Metro Hospital
14. Can international patients receive TAA treatment in India?
Yes, many Indian hospitals have dedicated international patient services to assist with medical visas, travel arrangements, accommodation, and treatment plans for international patients.
15. What should I do if I experience symptoms of a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
If you experience severe chest or back pain, shortness of breath, or any other concerning symptoms, seek immediate medical attention as these could be signs of a ruptured or dissecting aneurysm, which is a medical emergency.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of thoracic aortic aneurysm, from its causes and symptoms to the treatment options and postoperative care, is crucial for patients and their families. With advanced medical facilities and experienced healthcare professionals, India offers comprehensive care for TAA, making it a viable option for both domestic and international patients. Regular follow-ups and lifestyle modifications post-surgery are essential for a successful recovery and long-term health.
Top Doctors
Top Hospitals
THORACIC AORTIC ANEURYSM SURGERY COST IN INDIA

Duration of Treatment
5 to 7 hours
Days of Stay
5 to 10 Days
Anesthesia
as per advised
Cost
15000 t0 35000 USD
How Much Does Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery Cost in India?
Are you looking for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery Cost in India at one of the best hospitals at an affordable cost"? Here, we answer the question and explain how to choose the top Cardiac surgeon for better results. To make an appointment, call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782
We have shortlisted the list of the top cardiac Hospitals and Surgeons based on Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of surgeons, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery Cost in India: starting from 15000 to 35000 USD.
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD (as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day)
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day).
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will plan after the fresh evaluation reports.
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery Cost in India can vary as per the diagnosis, patient's conditions, surgeon experience, Implant quality, hospital facilities, and city.
- To make an appointment, learn more about the treatment, read the below information, or call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782. Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
The Top 10 Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgeons in India:
- Dr. Naresh Trehan
- Dr. Ramakanta Panda
- Dr. Devi Prasad Shetty
- Dr. S. K. Sinha
- Dr. Yugal K. Mishra
- Dr. Rajesh Sharma
- Dr. K. R. Balakrishnan
- Dr. Ashok Seth
- Dr. C. P. S. Chauhan
- Dr. Sandeep Attawar
Which is the Best Hospital for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery in India?
- MANIPAL HOSPITAL
- BLK HOSPITAL
- MAX HOSPITAL
- JAYPEE HOSPITAL
- APOLLO HOSPITAL
- FORTIS ESCORT HOSPITAL
- GLOBAL HOSPITAL
- HCG CANCER HOSPITAL
- ARTEMIS HOSPITAL
- MEDANTA HOSPITAL
- ASTER HOSPITAL
- YASHODHA HOSPITAL
- GLOBAL HOSPITAL
- NARAYANA HOSPITAL
Why you choose Peace Medical Tourism?
We are one of the best health care services providers for more than 10 years of experience to provide the best treatment at an affordable cost and guide our international patients to choose the top destination as per patient's budget and treatment.
- Comprehensive and 100% transparency.
- Help to Choose the Best Option for Cancer Treatment.
- Very highly skilled surgeon in India team.
- World-class technology for surgery.
- The high success rate of procedures with international standards.
- Affordable Cost of surgery.
What is a Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm?
A thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) is a bulging or dilation in the wall of the thoracic aorta, the part of the aorta that runs through the chest. The aorta is the largest artery in the body, responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. When the wall of the aorta weakens, it can balloon outward, forming an aneurysm. If left untreated, a thoracic aortic aneurysm can rupture, leading to life-threatening internal bleeding.
Types of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms
Thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) can be classified based on their location, shape, and underlying cause. Understanding the different types helps in determining the appropriate treatment approach and management strategy. Here’s a detailed look at the various types of thoracic aortic aneurysms:
Based on Location
-
Ascending Aortic Aneurysm
- Location: Occurs in the ascending aorta, the section of the aorta that rises from the heart’s left ventricle.
- Common Causes: Marfan syndrome, bicuspid aortic valve, and other genetic conditions.
- Risks: High risk of rupture and aortic dissection.
-
Aortic Arch Aneurysm
- Location: Found in the aortic arch, the curved portion of the aorta that gives rise to branches supplying blood to the head, neck, and arms.
- Common Causes: Atherosclerosis, trauma, and congenital conditions.
- Risks: Can affect blood flow to the brain and upper body, leading to complications like stroke.
-
Descending Aortic Aneurysm
- Location: Located in the descending thoracic aorta, which extends downward from the aortic arch through the chest.
- Common Causes: Atherosclerosis, hypertension, and trauma.
- Risks: May extend into the abdominal aorta, potentially causing abdominal aortic aneurysms.
Based on Shape
-
Fusiform Aneurysm
- Shape: Uniform, spindle-shaped dilation that involves the entire circumference of the aortic wall.
- Characteristics: Commonly found in the descending aorta.
- Risks: Generally grow slowly but can still rupture if they become too large.
-
Saccular Aneurysm
- Shape: Localized, balloon-like outpouching on one side of the aorta.
- Characteristics: More prone to rupture compared to fusiform aneurysms due to their asymmetrical shape.
- Risks: Often associated with trauma, infections, or certain genetic conditions.
Based on Underlying Cause
-
Genetic and Congenital Aneurysms
- Causes: Conditions like Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, and bicuspid aortic valve.
- Characteristics: These aneurysms typically develop at a younger age and may be associated with other connective tissue disorders.
- Risks: High risk of rapid growth and rupture.
-
Degenerative Aneurysms
- Causes: Age-related degeneration of the aortic wall, often due to atherosclerosis and hypertension.
- Characteristics: More common in older adults.
- Risks: Gradual enlargement with potential for rupture if untreated.
-
Traumatic Aneurysms
- Causes: Result from injury to the chest, such as from a car accident or fall.
- Characteristics: Can occur at any point in the thoracic aorta.
- Risks: May develop quickly and require immediate medical attention.
-
Infectious (Mycotic) Aneurysms
- Causes: Infections that weaken the aortic wall, such as bacterial endocarditis or syphilis.
- Characteristics: Often saccular and located in the descending aorta.
- Risks: High risk of rupture and need for prompt treatment with antibiotics and possibly surgery.
-
Inflammatory Aneurysms
- Causes: Chronic inflammatory conditions like Takayasu arteritis or giant cell arteritis.
- Characteristics: Inflammation causes thickening and weakening of the aortic wall.
- Risks: Can lead to rapid growth and rupture if inflammation is not controlled.
Additional Considerations
-
Pseudoaneurysms (False Aneurysms)
- Causes: Result from a tear in the aortic wall leading to a contained rupture. Unlike true aneurysms, which involve all three layers of the aortic wall, pseudoaneurysms are contained by the outer layers or surrounding tissues.
- Characteristics: Often occur due to trauma or surgical complications.
- Risks: High risk of rupture and require urgent treatment.
-
Dissecting Aneurysms
- Causes: Aortic dissection, where a tear in the inner layer of the aorta causes blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, leading to the formation of a false lumen.
- Characteristics: Can occur anywhere in the aorta and are classified based on the location and extent of the dissection.
- Risks: Highly dangerous and can lead to aortic rupture, organ damage, and death if not treated promptly.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Early diagnosis and regular monitoring are crucial for managing thoracic aortic aneurysms. Diagnostic tools include:
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart and aorta.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the aorta.
- MRI: Offers detailed images without radiation exposure.
- Angiography: Involves injecting a contrast dye into the bloodstream to visualize the aorta.
symptoms
Symptoms forThoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
TAAs often grow slowly and might not cause symptoms until they are large or ruptured. Symptoms, when present, may include:
-
Chest or back pain
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing or hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
risk factors
Risk Factors of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery, whether it is open surgery or endovascular repair, carries significant risks due to the complexity of the procedure and the critical nature of the aorta. Understanding these risks is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions and prepare adequately for the surgery. Below are the key risk factors associated with thoracic aortic aneurysm surgery:
General Surgical Risks
-
Bleeding
- Excessive bleeding during or after surgery is a common risk, especially given the large blood vessels involved.
-
Infection
- Risk of infection at the incision site or within the chest cavity.
-
Reactions to Anesthesia
- Allergic reactions or complications arising from general anesthesia.
-
Blood Clots
- Formation of blood clots that can lead to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism.
Specific Risks Related to TAA Surgery
-
Aortic Dissection
- A tear in the aorta's inner layer can occur, leading to a life-threatening condition where blood flows between the layers of the aorta wall.
-
Rupture of the Aneurysm
- During the procedure, there is a risk of the aneurysm rupturing, which can cause severe internal bleeding.
-
Graft Leakage or Failure
- The synthetic graft used to replace the aneurysmal section of the aorta may leak or fail, leading to complications.
-
Stroke
- A stroke can occur if blood flow to the brain is disrupted during the surgery.
-
Spinal Cord Injury
- Risk of spinal cord injury due to decreased blood supply, potentially resulting in paralysis or other neurological deficits.
-
Heart Attack
- The stress of surgery can precipitate a heart attack, particularly in patients with existing heart conditions.
Risk Factors Related to Patient Health
-
Age
- Older patients generally face higher surgical risks due to decreased physiological resilience.
-
Pre-existing Conditions
- Conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) increase surgical risks.
-
Previous Cardiac Surgeries
- Patients with a history of cardiac surgeries have increased risks due to scar tissue and previous alterations in anatomy.
-
Genetic Conditions
- Conditions like Marfan syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which affect connective tissue, can complicate surgery.
Technical and Procedure-Related Risks
-
Complex Anatomy
- Variations in the anatomy of the aorta or surrounding structures can increase the difficulty of the surgery.
-
Duration of Surgery
- Longer surgical times are associated with higher risks of complications such as infection, bleeding, and organ dysfunction.
-
Experience of the Surgical Team
- The skill and experience of the surgical team play a critical role in minimizing risks.
Post-Surgical Risks
-
Respiratory Complications
- Risk of pneumonia or other respiratory issues due to prolonged immobility or the effects of anesthesia.
-
Kidney Dysfunction
- Potential for acute kidney injury due to decreased blood flow or use of contrast dyes during imaging procedures.
-
Delayed Healing
- Factors such as poor nutrition, diabetes, or smoking can delay wound healing and increase the risk of infection.
-
Recurrent Aneurysms
- There is a risk that new aneurysms may develop in other sections of the aorta, necessitating further monitoring and potential future surgeries.
preparation
Preparation for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
Preparing for thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery involves multiple steps to ensure the patient's safety and improve the chances of a successful outcome. The preparation process includes a thorough medical evaluation, optimization of health conditions, and psychological readiness. Here’s a detailed guide on how to prepare for TAA surgery:
Medical Evaluation and Diagnostics
-
Comprehensive Medical History
- Review of personal and family medical history.
- Assessment of symptoms and risk factors.
-
Physical Examination
- Detailed physical examination focusing on cardiovascular health.
-
Imaging Studies
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the aorta to assess the size and location of the aneurysm.
- MRI: Offers detailed imaging without radiation exposure.
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to create images of the heart and aorta.
- Angiography: Involves injecting contrast dye to visualize the aorta and identify the aneurysm.
-
Laboratory Tests
- Blood tests to assess overall health, including kidney function, liver function, and blood clotting ability.
- Urine tests to check for kidney function and other underlying conditions.
-
Cardiovascular Assessment
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the electrical activity of the heart.
- Stress Test: Evaluates how the heart performs under physical stress.
- Cardiac Catheterization: Examines the coronary arteries for any blockages.
Optimizing Health Conditions
-
Blood Pressure Control
- Manage hypertension with medications and lifestyle changes to reduce stress on the aorta.
-
Blood Sugar Management
- Control diabetes through diet, medication, and monitoring blood sugar levels.
-
Smoking Cessation
- Quit smoking to improve lung function and blood circulation.
-
Nutritional Optimization
- Maintain a balanced diet to ensure adequate nutrition for healing.
- Consider supplements if necessary, as advised by a healthcare provider.
-
Weight Management
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of complications.
-
Medications
- Adjust or stop certain medications as directed by the surgeon.
- Start any new medications prescribed to optimize health before surgery.
Psychological and Emotional Preparation
-
Patient Education
- Understand the nature of the surgery, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
- Discuss the procedure, recovery process, and long-term care with the surgical team.
-
Support System
- Arrange for family or friends to provide support during the hospital stay and recovery period.
- Consider counseling or support groups for emotional support.
-
Preoperative Instructions
- Follow specific instructions provided by the surgical team, including fasting guidelines and medication adjustments.
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Cost in India
Hospital and Surgical Preparation
-
Preoperative Appointment
- Attend a preoperative appointment for final assessments and to address any questions or concerns.
-
Consent Form
- Sign informed consent forms after discussing the surgery with the healthcare team.
-
Packing for the Hospital
- Pack necessary items for the hospital stay, including comfortable clothing, personal hygiene items, and any prescribed medications.
-
Transportation Arrangements
- Arrange for transportation to and from the hospital.
-
Advance Directives
- Prepare advance directives, such as a living will or durable power of attorney for healthcare, if desired.
Day Before Surgery
-
Fasting
- Follow fasting instructions, typically no food or drink after midnight before the surgery.
-
Medication
- Take any prescribed medications as directed, with a small sip of water if allowed.
-
Hygiene
- Bathe or shower using antibacterial soap to reduce the risk of infection.
-
Rest
- Get a good night’s sleep to ensure the body is well-rested for surgery.
Day of Surgery
-
Arrival at the Hospital
- Arrive at the hospital on time as instructed.
- Check-in and complete any remaining paperwork.
-
Preoperative Area
- Change into a hospital gown and prepare for surgery.
- Meet with the surgical team, including the anesthesiologist, to review the procedure.
-
Intravenous (IV) Line
- An IV line will be placed to administer medications and fluids.
-
Final Checks
- Final health checks and discussions with the surgical team.
procedure
Procedures for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
Thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery involves various procedures tailored to the aneurysm's location, size, and the patient's overall health. The primary surgical procedures include open surgical repair and endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). Each procedure has its specific indications, steps, and recovery processes.
1. Open Surgical Repair
Indications:
- Large aneurysms (>5.5 cm in diameter) or rapidly growing aneurysms.
- Symptomatic aneurysms.
- Aneurysms with a high risk of rupture.
Procedure:
-
Anesthesia and Incision:
- The patient is placed under general anesthesia.
- An incision is made in the chest. The location of the incision (sternotomy or thoracotomy) depends on the aneurysm's position.
-
Exposure and Clamping:
- The aorta is exposed by carefully retracting tissues.
- Blood flow through the aorta is temporarily stopped using clamps placed above and below the aneurysm.
-
Aneurysm Resection:
- The aneurysmal section of the aorta is removed.
- The area is prepared for graft placement.
-
Graft Placement:
- A synthetic graft, usually made of Dacron or PTFE, is sewn into place to replace the removed section of the aorta.
- The clamps are slowly removed to restore blood flow through the graft.
-
Closure:
- The chest is closed in layers, and the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU) for monitoring.
Recovery:
- Initial recovery in the ICU for close monitoring.
- Pain management, respiratory therapy, and gradual mobilization.
- Hospital stay of about 7-10 days, with full recovery taking several weeks to months.
2. Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR)
Indications:
- Suitable for patients with anatomically favorable aneurysms.
- Patients at high risk for open surgery due to other medical conditions.
Procedure:
-
Anesthesia:
- The patient is usually placed under general anesthesia, though some cases may use regional anesthesia.
-
Access:
- Small incisions are made in the groin to access the femoral arteries.
-
Catheter Insertion:
- Catheters and guidewires are inserted through the femoral arteries and guided to the site of the aneurysm using fluoroscopic imaging.
-
Stent-Graft Deployment:
- A stent-graft is delivered via the catheter to the site of the aneurysm.
- The stent-graft is deployed and expanded to reinforce the aortic wall and exclude the aneurysm from blood flow.
-
Sealing and Verification:
- The stent-graft is positioned to ensure a tight seal above and below the aneurysm.
- Imaging is used to verify proper placement and seal.
-
Closure:
- The femoral artery incisions are closed, and the patient is monitored for any immediate complications.
Recovery:
- Shorter ICU stay compared to open surgery.
- Hospital discharge typically within 2-3 days.
- Faster overall recovery, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few weeks.
3. Hybrid Procedures
Indications:
- Complex aneurysms that involve multiple sections of the aorta.
- Patients with a combination of thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysms.
Procedure:
-
Combination of Open and Endovascular Techniques:
- Involves initial open surgical exposure followed by endovascular stent-graft placement.
-
Sequential Approach:
- May require staged procedures to address different sections of the aorta.
Recovery:
- Depends on the extent and combination of procedures performed.
- Typically involves longer recovery compared to EVAR but shorter than extensive open repairs.
4. Adjunct Procedures
-
Valve-Sparing Aortic Root Replacement (David Procedure):
- Indicated for aneurysms involving the aortic root.
- Preserves the patient’s native aortic valve while replacing the aneurysmal aortic root with a graft.
-
Bentall Procedure:
- Indicated for aneurysms involving the aortic root and valve.
- Involves replacement of the aortic valve, aortic root, and ascending aorta with a composite graft.
-
Frozen Elephant Trunk Procedure:
- Combines open surgical and endovascular techniques to treat extensive aneurysms involving the aortic arch and descending aorta.
- Uses a hybrid graft that is partially sewn in place and partially deployed endovascularly.
Preoperative and Postoperative Care
Preoperative:
- Comprehensive medical evaluation, including imaging studies.
- Optimization of medical conditions (e.g., controlling blood pressure, managing diabetes).
- Patient education and consent.
- Psychological support and preparation.
Postoperative:
- Intensive monitoring in the ICU for hemodynamic stability and complications.
- Pain management and respiratory therapy.
- Gradual mobilization and physical therapy.
- Regular follow-up with imaging to monitor graft integrity and aortic health.
Conclusion
Thoracic aortic aneurysm surgery includes various procedures, each tailored to the patient's specific condition and the aneurysm's characteristics. Open surgical repair, endovascular aneurysm repair, hybrid procedures, and adjunct techniques all play roles in managing TAAs. Comprehensive preoperative preparation, meticulous surgical execution, and diligent postoperative care are crucial for successful outcomes.
post procedure
Postoperative Management for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
Postoperative management for thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery is crucial to ensure successful recovery, minimize complications, and promote long-term health. This involves a multi-disciplinary approach with careful monitoring, medication management, physical therapy, and patient education. Below are the key aspects of postoperative management:
Immediate Postoperative Care
-
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Monitoring
- Hemodynamic Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen levels, and central venous pressure.
- Ventilation Support: Mechanical ventilation may be required initially to support breathing.
- Pain Management: Administration of pain relief medications through intravenous (IV) lines or patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pumps.
-
Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
- IV Fluids: Carefully monitored to maintain hydration and electrolyte balance.
- Urine Output: Monitored closely to ensure adequate kidney function.
-
Blood Management
- Transfusions: Blood or blood products may be given if needed to manage anemia or blood loss.
- Anticoagulation: Use of anticoagulants may be started to prevent blood clots, as per the surgical team's recommendations.
-
Respiratory Care
- Incentive Spirometry: Encouraged to prevent atelectasis and promote lung expansion.
- Chest Physiotherapy: To aid in clearing secretions and improve respiratory function.
-
Cardiac Monitoring
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Continuous ECG monitoring to detect any cardiac arrhythmias.
- Echocardiogram: Performed as needed to assess heart function post-surgery.
Intermediate Postoperative Care
-
Transition from ICU to Step-Down Unit
- Stabilization: Once stable, patients are transferred from the ICU to a step-down unit for continued monitoring.
- Gradual Mobilization: Initiation of gentle physical activity, such as sitting up in bed and short walks, to prevent complications from immobility.
-
Pain Management
- Oral Medications: Transition from IV pain medications to oral pain relief as the patient becomes more stable.
- Pain Assessment: Regular assessment of pain levels and adjustment of medications as needed.
-
Nutritional Support
- Diet Advancement: Gradual progression from liquids to a regular diet as tolerated.
- Nutritional Monitoring: Ensuring adequate caloric and protein intake to promote healing.
-
Wound Care
- Incision Care: Regular inspection and care of the surgical incision to prevent infection.
- Drain Management: Monitoring and removal of any surgical drains.
-
Physical Therapy
- Rehabilitation Exercises: Physical therapy sessions to improve strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular fitness.
- Breathing Exercises: Continued emphasis on respiratory exercises to improve lung function.
Long-Term Postoperative Care
-
Follow-Up Appointments
- Regular Check-Ups: Scheduled visits with the surgeon and cardiologist to monitor recovery and detect any complications early.
- Imaging Studies: Follow-up imaging (e.g., CT scans, MRIs) to monitor the repair site and ensure there are no new aneurysms or complications.
-
Medication Management
- Antihypertensives: Medications to control blood pressure and reduce stress on the aorta.
- Statins: To manage cholesterol levels and reduce cardiovascular risk.
- Anticoagulants/Antiplatelets: As prescribed to prevent blood clots.
-
Lifestyle Modifications
- Diet: A heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity tailored to the patient’s condition, avoiding strenuous activities that can increase blood pressure.
- Smoking Cessation: Strong emphasis on quitting smoking to promote vascular health.
-
Monitoring for Complications
- Aortic Dissection/Rupture: Being vigilant for symptoms such as sudden severe chest or back pain.
- Graft Complications: Monitoring for signs of graft infection, leakage, or failure.
- Kidney Function: Regular blood tests to monitor kidney function, especially if contrast agents were used during the procedure.
-
Emotional and Psychological Support
- Counseling: Psychological support or counseling to help cope with the stress and anxiety associated with major surgery.
- Support Groups: Participation in support groups for patients with similar conditions to share experiences and encouragement.
Emergency Signs to Watch For
- Severe Chest Pain: Sudden, intense pain in the chest, back, or abdomen.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing.
- Neurological Symptoms: Sudden weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking.
- Swelling or Redness: At the incision site, indicating potential infection
success rate
Success Rate of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
The success rate of thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) surgery varies based on several factors, including the type of surgery (open or endovascular), the patient’s overall health, the aneurysm’s size and location, and the experience of the surgical team. Generally, both open surgical repair and endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) have high success rates, but each comes with its own risks and benefits.
Open Surgical Repair Success Rates
-
General Success Rate:
- Open surgical repair of TAA typically has a success rate ranging from 90% to 95% in centers of excellence with experienced surgical teams.
-
Factors Influencing Success:
- Patient Age and Health: Younger patients with fewer comorbidities tend to have better outcomes.
- Aneurysm Size and Location: Smaller aneurysms and those located in less complex anatomical regions generally have higher success rates.
- Surgical Experience: Surgeons and centers with more experience in performing open TAA repairs tend to have better success rates and fewer complications.
-
Long-Term Outcomes:
- Patients typically enjoy a good quality of life post-surgery, with a low incidence of aneurysm recurrence in the repaired segment.
- Regular follow-ups and imaging are essential to monitor for any potential complications or new aneurysm formations.
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) Success Rates
-
General Success Rate:
- EVAR for TAA has a success rate of approximately 95% to 98%, making it slightly higher than open surgery due to its less invasive nature and lower immediate risk profile.
-
Factors Influencing Success:
- Anatomical Suitability: Patients whose aneurysms are anatomically suitable for EVAR tend to have higher success rates.
- Patient Health: Better overall health and fewer comorbid conditions improve outcomes.
- Technological Advancements: Advances in stent-graft technology and imaging techniques have improved the success rates of EVAR procedures.
-
Long-Term Outcomes:
- EVAR patients generally have quicker recoveries and shorter hospital stays compared to open surgery.
- Long-term follow-up is crucial to monitor the integrity of the stent-graft and ensure there are no endoleaks or other complications.
Comparative Success Rates and Considerations
-
Perioperative Mortality:
- Open Surgery: The perioperative mortality rate (death within 30 days of surgery) ranges from 5% to 10%.
- EVAR: The perioperative mortality rate is lower, typically around 1% to 5%.
-
Complication Rates:
- Open Surgery: Higher risk of complications such as bleeding, infection, and prolonged recovery time.
- EVAR: Lower immediate complication rates, but long-term monitoring for stent-graft complications is essential.
-
Hospital Stay and Recovery:
- Open Surgery: Longer hospital stays (7-10 days) and recovery periods (several weeks to months).
- EVAR: Shorter hospital stays (2-3 days) and quicker recovery (a few weeks).
-
Reintervention Rates:
- Open Surgery: Lower reintervention rates due to the durable nature of the surgical repair.
- EVAR: Higher reintervention rates due to potential issues with the stent-graft, such as migration or endoleaks.
Conclusion
Both open surgical repair and endovascular aneurysm repair for thoracic aortic aneurysms have high success rates, typically ranging from 90% to 98%. The choice between the two depends on various factors, including the patient’s health, the aneurysm’s characteristics, and the expertise of the surgical team. Open surgery offers long-term durability but comes with higher immediate risks and longer recovery, while EVAR provides a less invasive option with quicker recovery but requires ongoing monitoring for potential complications. The success of either procedure is enhanced by careful patient selection, thorough preoperative planning, and diligent postoperative care.
faqs from doctor
FAQs for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm in India
1. What is a thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA)?
A thoracic aortic aneurysm is an abnormal bulging or ballooning in the wall of the thoracic aorta, the major artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. It can lead to serious complications if it ruptures or dissects.
2. What causes a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
The primary causes include:
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
- Genetic conditions (e.g., Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome)
- High blood pressure
- Trauma or injury to the chest
- Infections affecting the aorta
3. What are the symptoms of a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
Many TAAs are asymptomatic, but symptoms can include:
- Chest pain or back pain
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing or hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
4. How is a thoracic aortic aneurysm diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical examination
- Imaging tests such as a chest X-ray, CT scan, MRI, or echocardiogram
- Angiography to visualize the aorta
5. What are the treatment options for a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
Treatment options depend on the size and growth rate of the aneurysm and the patient's overall health:
- Monitoring: Small, asymptomatic aneurysms may be monitored with regular imaging tests.
- Medication: To control blood pressure and reduce the risk of aneurysm growth.
- Surgery: Options include open surgical repair and endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR).
6. What is open surgical repair?
Open surgical repair involves removing the aneurysmal section of the aorta and replacing it with a synthetic graft. This procedure is more invasive and requires a longer recovery period.
7. What is endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR)?
EVAR is a minimally invasive procedure where a stent-graft is inserted into the aorta via small incisions in the groin. The stent-graft reinforces the aortic wall and prevents the aneurysm from rupturing.
8. What are the risks associated with TAA surgery?
Risks include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Heart attack or stroke
- Graft complications (e.g., leakage, migration)
- Kidney damage
9. What is the recovery time after TAA surgery?
- Open Surgery: Hospital stay of 7-10 days with a full recovery period of several weeks to months.
- EVAR: Shorter hospital stay of 2-3 days with a recovery period of a few weeks.
10. How often should I follow up after TAA surgery?
Regular follow-ups are crucial. Patients typically need imaging tests every 6-12 months to monitor the repair and detect any potential complications early.
11. What lifestyle changes are recommended after TAA surgery?
- Diet: Adopt a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Exercise: Engage in regular, moderate exercise while avoiding strenuous activities.
- Smoking Cessation: Quit smoking to improve vascular health.
- Blood Pressure Management: Keep blood pressure under control with medication and lifestyle changes.
12. What is the cost of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm in India?
The cost can vary significantly depending on the hospital, surgeon, and specific procedure:
- Open Surgery: Typically ranges from 15000 to 30000 USD.
- EVAR: Generally ranges from 10,000 to 15000 USD.
13. Are there specialized centers for TAA treatment in India?
Yes, several hospitals in India are renowned for TAA treatment, including:
- Jaypee Hospital New Delhi
- Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, New Delhi
- Medanta - The Medicity, Gurgaon
- Apollo Hospitals, Chennai
- Narayana Health, Bangalore
- Max Hospital
- Metro Hospital
14. Can international patients receive TAA treatment in India?
Yes, many Indian hospitals have dedicated international patient services to assist with medical visas, travel arrangements, accommodation, and treatment plans for international patients.
15. What should I do if I experience symptoms of a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
If you experience severe chest or back pain, shortness of breath, or any other concerning symptoms, seek immediate medical attention as these could be signs of a ruptured or dissecting aneurysm, which is a medical emergency.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of thoracic aortic aneurysm, from its causes and symptoms to the treatment options and postoperative care, is crucial for patients and their families. With advanced medical facilities and experienced healthcare professionals, India offers comprehensive care for TAA, making it a viable option for both domestic and international patients. Regular follow-ups and lifestyle modifications post-surgery are essential for a successful recovery and long-term health.





























