Duration of Treatment
10-14 Hours Surgery
Days of Stay
21 Days
Anesthesia
General
Cost
40000 to 50000 USD
How Much Does Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India?
Are we looking for Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India or the best Hand Transplant Surgery Hospital in India at an affordable cost? Here, we answer the question and explain how to choose the top doctors for better results.
We have shortlisted the list of the best top Hand Transplant Surgery Hospitals and Surgeons based on Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of surgeons, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India: starting from 40000 to 50000 USD.
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD (as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day)
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day).
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will plan after the fresh evaluation reports.
- In India, Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India can vary as per the diagnosis, patient's conditions, Plastic surgeon experience, Implant quality, hospital facilities, and city.
- To make an appointment, learn more about the hand trasnplant, read the below information, or call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782. Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
Top 5 Best Hands Transplant Surgeon in India
There are five of the best hand transplant surgeons in India, known for their expertise and successful surgeries in this specialized field:
- Dr. Subramania Iyer - Head of the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi. He led the team that performed India's first double hand transplant in 2015.
- Dr. S. Raja Sabapathy - Chairman of the Department of Plastic, Hand, Reconstructive Microsurgery, and Burns at Ganga Hospital, Coimbatore. He is renowned for his expertise in hand and microsurgery.
- Dr Anubhav Gupta - Senior Consultant at the Department of Plastic, Aesthetic, and Reconstructive Surgery at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi. He has extensive experience and best hand transplant surgeon in India and reconstructive surgeries.
- Dr. Mohit Sharma - Senior Consultant at the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at Amrita Hospital. He specializes in complex hand and microsurgical procedures. He has +31 years of experience in the field. Dr. Mohit started the first Vascularised composite allotransplantation (VCA)programme in India in the year 2015. He Performed the first Successful hand Transplant in the world and is known as the best hand transplant surgeon in India.
- Dr. Nilesh Satbhai - Known for his remarkable achievements, including India's first successful bilateral hand transplant in a quadruple amputee and other pioneering hand transplant surgeries. He is a highly experienced and skillful plastic surgeon who has dedicated his career to helping patients feel at ease with their bodies. He completed his Plastic Surgery training at the prestigious Seth G. S. Medical College and K.E.M Hospital in Mumbai.
- The first successful bilateral hand transplant in Western India in August 2020
- India’s first successful bilateral hand transplant in a quadruple amputee recipient in October 2021
- India’s first successful partial hand transplant in February 2022
- India's first unilateral hand transplant and the first transplant done for congenital hand aplasia
These surgeons are recognized for their contributions to hand transplantation and their commitment to advancing medical techniques in this challenging area of surgery.
What is Hand Transplant surgery in India?
Hand transplant surgery, also known as vascularized composite allotransplantation (VCA), is a complex surgical procedure that involves transplanting a hand or hands from a deceased donor to a recipient who has lost one or both hands. Hand transplants are performed in a small number of transplant centers worldwide. More than 300 patients have received hand and arm transplants at institutions worldwide.
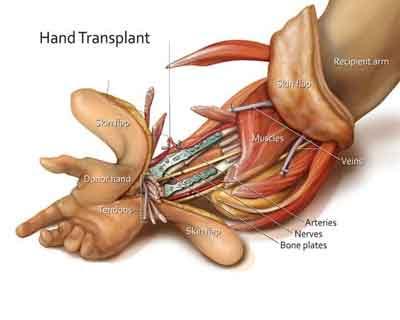
The intricate surgery involves connecting bones, blood vessels, nerves, muscles, tendons, and skin. The surgery can take 12 to 24 hours and involves a team of surgeons reattaching bones, arteries, veins, tendons, muscles, nerves, and skin.
Why Do You Need Hand Transplant Surgery?
Hand transplant surgery is considered for individuals who have lost one or both hands or have suffered severe loss of function due to injury, illness, or congenital conditions. Here are the primary reasons why someone might need hand transplant surgery:
1. Traumatic Amputation
- Accidents: Severe injuries from accidents (e.g., industrial accidents, car accidents) that result in the loss of one or both hands.
- Combat Injuries: Military personnel who lose hands due to combat-related injuries, such as explosions or gunshot wounds.
2. Medical Conditions
- Severe Infections: Infections that lead to gangrene or sepsis, necessitate amputation to save the patient’s life.
- Cancer: Surgical removal of hands due to malignancies that cannot be treated conservatively.
3. Congenital Conditions
- Birth Defects: Individuals born with severe hand deformities that significantly impair function and cannot be corrected with reconstructive surgery.
4. Loss of Function
- Nerve Damage: Extensive nerve damage from conditions like brachial plexus injuries that severely impair hand function.
- Severe Burns: Extensive burns that destroy the hand’s functional tissues beyond the possibility of repair or reconstruction.
5. Quality of Life Improvement
- Daily Activities: Improving the ability to perform daily tasks and enhance independence.
- Psychological Well-being: Improving self-esteem and mental health by restoring a more normal appearance and functionality.
Benefits of Hand Transplant Surgery
- Functional Improvement: Restoration of hand function, allowing the patient to perform daily activities, work, and engage in hobbies.
- Aesthetic Restoration: Improved appearance of the hand, which can significantly boost self-esteem and social interactions.
- Psychological Benefits: Enhanced quality of life, mental health, and overall well-being due to regained independence and functionality.
Considerations for Hand Transplant Surgery
- Lifelong Commitment: Requires a lifelong commitment to immunosuppressive therapy to prevent rejection.
- Risk of Complications: Potential risks include rejection, infection, and complications from immunosuppressive medications.
- Extensive Rehabilitation: Requires a long-term, intensive rehabilitation program to regain function and strength in the transplanted hand.
Conclusion
Hand transplant surgery can offer significant improvements in functionality, aesthetics, and quality of life for individuals who have lost their hands due to various reasons. It is a complex procedure that requires careful candidate selection, extensive pre-surgical planning, and long-term post-surgical care and rehabilitation.
What is The Risk Factor of Hand Transplant Surgery?
Hand transplant surgery, while potentially life-changing, comes with several risks and challenges. Here are the primary risks associated with the procedure:
1. Rejection
- Acute Rejection: The body's immune system may attack the transplanted hand shortly after surgery. This requires immediate medical intervention.
- Chronic Rejection: Long-term rejection can occur, leading to the gradual loss of function in the transplanted hand.
2. Infection
- Surgical Site Infections: The risk of infection at the site of surgery, which can complicate recovery.
- Systemic Infections: Immunosuppressive medications, necessary to prevent rejection, increase the risk of infections throughout the body.
3. Complications from Immunosuppressive Therapy
- Side Effects: Medications can cause side effects such as weight gain, diabetes, high blood pressure, and kidney damage.
- Increased Cancer Risk: Long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs can increase the risk of certain cancers.
4. Functional Recovery Challenges
- Limited Functionality: Not all patients regain full functionality, and the extent of functional recovery can vary widely.
- Prolonged Rehabilitation: Intensive and prolonged rehabilitation is required, and full recovery can take years.
5. Psychological Impact
- Adjustment Issues: Some patients may struggle with the psychological aspects of adapting to a transplanted hand, including body image and identity issues.
- Emotional Stress: The stress of ongoing medical treatments and the uncertainty of outcomes can be significant.
6. Technical Complications
- Vascular Problems: Issues with blood flow to the transplanted hand can lead to tissue death and failure of the transplant.
- Nerve Regeneration: Nerve healing and regeneration are slow processes, and incomplete nerve recovery can limit hand function.
7. Cost and Accessibility
- High Cost: The procedure is expensive, including the surgery itself, immunosuppressive medications, and rehabilitation.
- Limited Availability: Access to skilled surgical teams and donor hands can be limited, making the procedure less accessible.
Conclusion
Hand transplant surgery carries significant risks and requires a careful weighing of potential benefits against these risks. Candidates for the surgery undergo extensive evaluation to determine if they are suitable for the procedure and to prepare them for the challenges ahead. Close monitoring, rigorous medical care, and dedicated rehabilitation are essential to maximizing the chances of a successful outcome.
How to Prepare for Hand Transplant Surgery?
Preparation for hand transplant surgery is a comprehensive and multidisciplinary process designed to ensure the best possible outcome. Here's a detailed overview of the steps involved:
1. Medical Evaluation
- Comprehensive Health Assessment: A thorough physical examination and review of medical history to assess overall health and suitability for surgery.
- Blood Tests: Blood typing and cross-matching to ensure compatibility with potential donors.
- Immunological Tests: Tests to assess immune status and potential for rejection.
2. Psychological Evaluation
- Mental Health Assessment: Evaluations by psychologists or psychiatrists to ensure the candidate is mentally prepared for the challenges of the surgery and the long-term commitment required.
- Support System: Assessment of the patient's support system, including family and friends, to ensure they have adequate emotional and practical support.
3. Pre-Surgical Counseling
- Education on Risks and Benefits: Detailed discussions about the potential risks, benefits, and outcomes of the surgery.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: Information on the need for lifelong immunosuppressive medication and its potential side effects.
4. Physical Preparation
- Nutritional Optimization: Ensuring the patient is in optimal nutritional health to promote healing and recovery.
- Physical Conditioning: Pre-surgical physical therapy to maintain or improve the strength and flexibility of the residual limb and overall fitness.
5. Organizing Logistics
- Coordination with Transplant Team: Regular communication with the transplant team to coordinate the timing and logistics of the surgery.
- Hospital Preparation: Admission to the hospital and preparation of the surgical suite.
6. Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Informed Consent: Obtaining informed consent after ensuring the patient understands all aspects of the surgery.
- Ethical Approval: Ensuring that the transplant procedure has been reviewed and approved by relevant ethical committees.
7. Pre-Surgical Tests and Procedures
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans of the residual limb to plan the surgical approach.
- Vascular Studies: Assessing the blood vessels to ensure they can support the transplanted hand.
8. Pre-Operative Instructions
- Fasting: Instructions on fasting before surgery, typically starting from midnight on the day of the surgery.
- Medication Management: Guidance on which medications to take or avoid before surgery.
9. Developing a Post-Operative Plan
- Rehabilitation Plan: Arranging for post-operative rehabilitation, including physical and occupational therapy.
- Follow-Up Schedule: Planning regular follow-up visits to monitor the progress of the transplant and adjust medications as needed.
10. Challenges and Considerations
- Donor Availability: Finding suitable donors remains a challenge due to the need for specific tissue matching.
- Cost: Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India, covering surgery, post-operative care, and lifelong immunosuppressive therapy.
- Awareness and Accessibility: Increasing awareness about organ donation and improving accessibility to advanced medical facilities can enhance the success and reach of hand transplant surgeries in India.
- Best Hospitals : Searching the best Hand Transplant Surgery Hospital in India
Conclusion
Preparation for hand transplant surgery is a meticulous process that involves medical, psychological, and logistical planning. Ensuring that the patient is well-prepared physically, mentally, and emotionally is crucial for the success of the surgery and the subsequent recovery and rehabilitation. The involvement of a multidisciplinary team ensures that all aspects of the patient's health and well-being are addressed, increasing the chances of a positive outcome.
What is the procedures of Hand Transplant Surgery?
Hand transplant surgery is a complex and multidisciplinary procedure that involves multiple stages, from preoperative preparation to postoperative care. Here’s a detailed overview of the entire process:
Preoperative Preparation
- Medical and Psychological Evaluation:
- Comprehensive health assessment to determine overall suitability for surgery.
- Psychological evaluation to ensure mental preparedness for the procedure and the long-term commitment required.
- Donor Matching:
- Blood type and tissue compatibility testing.
- Identification and preparation of a suitable donor hand.
- Pre-Surgical Counseling:
- Discussions about the risks, benefits, and expected outcomes of the surgery.
- Information on the need for lifelong immunosuppressive therapy and its side effects.
- Physical Conditioning:
- Pre-surgical physical therapy to maintain or improve the strength and flexibility of the residual limb.
Surgical Procedure
- Anesthesia:
- General anesthesia is administered to the patient to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free during the procedure.
- Preparation of the Donor Hand:
- The donor hand is carefully harvested, preserving bones, tendons, blood vessels, nerves, and skin.
- The donor hand is kept in a cold, sterile solution to maintain its viability.
- Recipient Limb Preparation:
- The recipient’s residual limb is prepared for the transplant, including the removal of any non-viable tissue.
- Bone Fixation:
- The bones of the donor's hand are aligned and fixated to the recipient’s bones using plates and screws.
- Vascular Anastomosis:
- Blood vessels (arteries and veins) from the donor's hand are connected to those of the recipient using microsurgical techniques to restore blood flow.
- Nerve Repair:
- Major nerves are meticulously connected to allow for eventual sensation and motor function in the transplanted hand.
- Tendon and Muscle Attachment:
- Tendons and muscles are connected to enable movement and function of the hand.
- Skin Closure:
- The skin is carefully closed, and the hand is bandaged and immobilized to promote healing.
Postoperative Care
- Intensive Monitoring:
- Close monitoring in the ICU for signs of rejection, infection, and complications.
- Regular blood tests and imaging studies to assess the health of the transplanted hand.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy:
- Lifelong administration of immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection of the transplanted hand.
- Monitoring and managing side effects of immunosuppressive drugs.
- Rehabilitation:
- Intensive physical and occupational therapy to regain function and strength in the transplanted hand.
- Gradual increase in the use of the hand as healing progresses.
- Follow-Up Care:
- Regular follow-up visits to monitor progress, adjust medications, and address any issues.
- Psychological support to help with the adjustment to the transplanted hand.
Potential Complications
- Rejection: Acute or chronic rejection of the transplanted hand.
- Infection: Increased risk of infections due to immunosuppressive therapy.
- Functional Recovery: Variability in the degree of functional recovery and possible limitations in hand function.
- Complications from Immunosuppressive Therapy: Side effects such as weight gain, diabetes, high blood pressure, and increased risk of certain cancers.
Conclusion
Hand transplant surgery is a highly specialized and intricate procedure that requires careful planning, a skilled surgical team, and comprehensive postoperative care. The goal is to restore function and improve the quality of life for individuals who have lost their hands due to injury or illness. With advances in surgical techniques and immunosuppressive therapy, the success rates of hand transplants continue to improve, offering hope to many patients.
What is the success rate for surgery of hand transplant surgery?
The success rate for hand transplant surgery, also known as vascularized composite allotransplantation (VCA), varies based on several factors, including the patient's overall health, the extent of the injury, and adherence to postoperative care protocols. Here are some key points regarding the success rates and outcomes:
Success Rates and Outcomes
- Survival of the Transplanted Hand
- High Survival Rates: The majority of transplanted hands survive if there are no major complications and if the patient adheres to the immunosuppressive regimen. The survival rate for the transplanted hand is generally high, with most hands surviving at least 1-5 years post-transplant.
- Functional Outcomes
- Functional Recovery: Many patients regain significant function in their transplanted hands, including the ability to perform daily tasks, although the degree of functional recovery can vary widely.
- Sensation and Motor Skills: Recovery of sensation and motor skills occurs gradually and can take several months to years. Some patients achieve near-normal function, while others may experience limited movement and sensation.
- Rejection Episodes
- Management of Rejection: Acute rejection episodes are common but can often be managed successfully with adjustments to immunosuppressive therapy. Chronic rejection remains a long-term concern.
- Preventive Measures: Strict adherence to immunosuppressive medications and regular follow-up care are crucial in preventing and managing rejection.
Reported Success Rates
- Initial Success
- Short-Term Success: Initial success rates, defined as the survival of the transplanted hand and immediate postoperative recovery, are high, typically above 85-90%.
- Long-Term Success
- Long-Term Functionality: Long-term success rates, which take into account the functionality and health of the transplanted hand, vary. Studies report that around 60-80% of patients experience good to excellent functional outcomes several years post-transplant.
- Quality of Life: Many patients report significant improvements in quality of life and psychological well-being after a successful hand transplant.
Factors Influencing Success Rates
- Patient Selection
- Ideal Candidates: Patients who are in good overall health, have a strong psychological profile, and are motivated to adhere to postoperative care protocols tend to have better outcomes.
- Surgical Expertise
- Experienced Teams: Success rates are higher in medical centers with experienced surgical teams and comprehensive transplant programs.
- Postoperative Care
- Adherence to Therapy: Strict adherence to immunosuppressive therapy and participation in rehabilitation programs are critical for long-term success.
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent follow-up visits and monitoring for signs of rejection and complications improve outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations
- Immunosuppressive Therapy
- Side Effects: Long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs can lead to significant side effects, including increased risk of infections and certain cancers.
- Rehabilitation
- Intensive and Long-Term: Extensive and prolonged rehabilitation is required to maximize functional recovery, which can be challenging for some patients.
Conclusion
The success rate for hand transplant surgery is generally favorable, with high initial success rates and promising long-term outcomes for many patients. The overall success depends on various factors, including patient selection, surgical expertise, adherence to immunosuppressive therapy, and comprehensive postoperative care. Despite the challenges, hand transplant surgery can significantly improve the quality of life and functional abilities of individuals who have lost their hands due to injury or illness.
FAQs for surgery of hand transplant surgery?
1. What is hand transplant surgery?
Hand transplant surgery, also known as vascularized composite allotransplantation (VCA), involves transplanting a hand or hands from a deceased donor to a recipient who has lost one or both hands. It requires the connection of bones, blood vessels, nerves, tendons, muscles, and skin.
2. Who is a candidate for hand transplant surgery?
Candidates typically include individuals who have lost one or both hands due to traumatic injury, infection, or medical conditions such as cancer. They must be in good overall health, mentally prepared, and committed to lifelong immunosuppressive therapy and extensive rehabilitation.
3. How are donors selected for hand transplant surgery?
Donor hands are selected based on blood type and tissue compatibility with the recipient. The donor hand must come from a deceased donor, and matching is crucial to minimize the risk of rejection.
4. What are the risks associated with hand transplant surgery?
- Rejection: Acute or chronic rejection of the transplanted hand.
- Infection: Increased risk due to immunosuppressive medications.
- Complications from Immunosuppressive Therapy: Side effects like weight gain, diabetes, high blood pressure, and increased cancer risk.
- Functional Recovery: Variability in the degree of regained function.
5. What is the success rate of hand transplant surgery?
Initial success rates, defined by the survival of the transplanted hand and immediate recovery, are high, typically above 85-90%. Long-term success rates, considering functionality and health of the hand, are around 60-80% several years post-transplant. And you need the Best Hand Transplant Surgeon in India for good results.
6. What does the surgical procedure involve?
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered.
- Donor Hand Preparation: The donor's hand is harvested and preserved.
- Recipient Limb Preparation: The residual limb is prepared.
- Bone Fixation: Bones are aligned and fixed.
- Vascular Anastomosis: Blood vessels are connected.
- Nerve Repair: Nerves are connected.
- Tendon and Muscle Attachment: Tendons and muscles are attached.
- Skin Closure: The skin is closed and the hand is bandaged.
7. What is the recovery process like after hand transplant surgery?
Recovery involves intensive monitoring for signs of rejection and complications, lifelong immunosuppressive therapy, and extensive physical and occupational therapy to regain function and strength. Regular follow-up visits are necessary to monitor progress and adjust medications.
8. How long is the rehabilitation process?
Rehabilitation is a long-term commitment and can take several months to years. It involves regular physical and occupational therapy to improve the function, strength, and dexterity of the transplanted hand.
9. What are the potential complications of immunosuppressive therapy?
- Infections: Increased susceptibility to infections.
- Side Effects: Weight gain, diabetes, high blood pressure, and increased risk of certain cancers.
- Organ Damage: Potential damage to organs like the kidneys and liver over long-term use.
10. How can patients improve the chances of a successful hand transplant?
- Adherence to Therapy: Strict adherence to immunosuppressive medication regimens.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Frequent visits to the transplant team for monitoring and adjustments.
- Rehabilitation Commitment: Active participation in rehabilitation programs.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support overall well-being.
11. Can a transplanted hand perform normal functions?
Many patients regain significant function, including the ability to perform daily tasks. However, the extent of functional recovery varies, and some may experience limitations in movement and sensation.
12. What is the long-term outlook for patients with a hand transplant?
With proper medical care, adherence to immunosuppressive therapy, and ongoing rehabilitation, many patients experience improved quality of life and functional abilities. Long-term success requires a lifelong commitment to health management.
13. How much cost will come for hand transplant Surgery in India?
The cost of hand transplant surgery in India can vary widely based on several factors, including the medical facility, the complexity of the surgery, the length of the hospital stay, postoperative care, and the need for lifelong immunosuppressive therapy. Here is a breakdown of the potential costs involved:
While it is difficult to provide an exact figure, here are some estimated costs based on typical expenses:
- Initial Surgery and Hospitalization
- Surgery and Immediate Hospitalization: ?20,00,000 to ?40,00,000 (approximately $25,000 to $50,000)
- ICU Stay: Additional costs depending on the duration of stay and level of care required
- Immunosuppressive Medications
- Monthly Costs: ?10,000 to ?50,000 (approximately $125 to $625) per month for lifelong immunosuppressive therapy
- Rehabilitation
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: ?50,000 to ?2,00,000 (approximately $625 to $2,500)
Conclusion
Hand transplant surgery offers a potential solution for individuals who have lost their hands, providing the possibility of restoring function and improving quality of life. However, it requires careful candidate selection, meticulous surgical technique, comprehensive postoperative care, and a strong commitment from the patient to adhere to treatment protocols.
Top Doctors
Top Hospitals
HAND TRANSPLANT SURGERY COST IN INDIA

Duration of Treatment
10-14 Hours Surgery
Days of Stay
21 Days
Anesthesia
General
Cost
40000 to 50000 USD
How Much Does Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India?
Are we looking for Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India or the best Hand Transplant Surgery Hospital in India at an affordable cost? Here, we answer the question and explain how to choose the top doctors for better results.
We have shortlisted the list of the best top Hand Transplant Surgery Hospitals and Surgeons based on Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of surgeons, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India: starting from 40000 to 50000 USD.
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD (as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day)
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day).
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will plan after the fresh evaluation reports.
- In India, Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India can vary as per the diagnosis, patient's conditions, Plastic surgeon experience, Implant quality, hospital facilities, and city.
- To make an appointment, learn more about the hand trasnplant, read the below information, or call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782. Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
Top 5 Best Hands Transplant Surgeon in India
There are five of the best hand transplant surgeons in India, known for their expertise and successful surgeries in this specialized field:
- Dr. Subramania Iyer - Head of the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi. He led the team that performed India's first double hand transplant in 2015.
- Dr. S. Raja Sabapathy - Chairman of the Department of Plastic, Hand, Reconstructive Microsurgery, and Burns at Ganga Hospital, Coimbatore. He is renowned for his expertise in hand and microsurgery.
- Dr Anubhav Gupta - Senior Consultant at the Department of Plastic, Aesthetic, and Reconstructive Surgery at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi. He has extensive experience and best hand transplant surgeon in India and reconstructive surgeries.
- Dr. Mohit Sharma - Senior Consultant at the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at Amrita Hospital. He specializes in complex hand and microsurgical procedures. He has +31 years of experience in the field. Dr. Mohit started the first Vascularised composite allotransplantation (VCA)programme in India in the year 2015. He Performed the first Successful hand Transplant in the world and is known as the best hand transplant surgeon in India.
- Dr. Nilesh Satbhai - Known for his remarkable achievements, including India's first successful bilateral hand transplant in a quadruple amputee and other pioneering hand transplant surgeries. He is a highly experienced and skillful plastic surgeon who has dedicated his career to helping patients feel at ease with their bodies. He completed his Plastic Surgery training at the prestigious Seth G. S. Medical College and K.E.M Hospital in Mumbai.
- The first successful bilateral hand transplant in Western India in August 2020
- India’s first successful bilateral hand transplant in a quadruple amputee recipient in October 2021
- India’s first successful partial hand transplant in February 2022
- India's first unilateral hand transplant and the first transplant done for congenital hand aplasia
These surgeons are recognized for their contributions to hand transplantation and their commitment to advancing medical techniques in this challenging area of surgery.
What is Hand Transplant surgery in India?
Hand transplant surgery, also known as vascularized composite allotransplantation (VCA), is a complex surgical procedure that involves transplanting a hand or hands from a deceased donor to a recipient who has lost one or both hands. Hand transplants are performed in a small number of transplant centers worldwide. More than 300 patients have received hand and arm transplants at institutions worldwide.
The intricate surgery involves connecting bones, blood vessels, nerves, muscles, tendons, and skin. The surgery can take 12 to 24 hours and involves a team of surgeons reattaching bones, arteries, veins, tendons, muscles, nerves, and skin.
symptoms
Why Do You Need Hand Transplant Surgery?
Hand transplant surgery is considered for individuals who have lost one or both hands or have suffered severe loss of function due to injury, illness, or congenital conditions. Here are the primary reasons why someone might need hand transplant surgery:
1. Traumatic Amputation
- Accidents: Severe injuries from accidents (e.g., industrial accidents, car accidents) that result in the loss of one or both hands.
- Combat Injuries: Military personnel who lose hands due to combat-related injuries, such as explosions or gunshot wounds.
2. Medical Conditions
- Severe Infections: Infections that lead to gangrene or sepsis, necessitate amputation to save the patient’s life.
- Cancer: Surgical removal of hands due to malignancies that cannot be treated conservatively.
3. Congenital Conditions
- Birth Defects: Individuals born with severe hand deformities that significantly impair function and cannot be corrected with reconstructive surgery.
4. Loss of Function
- Nerve Damage: Extensive nerve damage from conditions like brachial plexus injuries that severely impair hand function.
- Severe Burns: Extensive burns that destroy the hand’s functional tissues beyond the possibility of repair or reconstruction.
5. Quality of Life Improvement
- Daily Activities: Improving the ability to perform daily tasks and enhance independence.
- Psychological Well-being: Improving self-esteem and mental health by restoring a more normal appearance and functionality.
Benefits of Hand Transplant Surgery
- Functional Improvement: Restoration of hand function, allowing the patient to perform daily activities, work, and engage in hobbies.
- Aesthetic Restoration: Improved appearance of the hand, which can significantly boost self-esteem and social interactions.
- Psychological Benefits: Enhanced quality of life, mental health, and overall well-being due to regained independence and functionality.
Considerations for Hand Transplant Surgery
- Lifelong Commitment: Requires a lifelong commitment to immunosuppressive therapy to prevent rejection.
- Risk of Complications: Potential risks include rejection, infection, and complications from immunosuppressive medications.
- Extensive Rehabilitation: Requires a long-term, intensive rehabilitation program to regain function and strength in the transplanted hand.
Conclusion
Hand transplant surgery can offer significant improvements in functionality, aesthetics, and quality of life for individuals who have lost their hands due to various reasons. It is a complex procedure that requires careful candidate selection, extensive pre-surgical planning, and long-term post-surgical care and rehabilitation.
risk factors
What is The Risk Factor of Hand Transplant Surgery?
Hand transplant surgery, while potentially life-changing, comes with several risks and challenges. Here are the primary risks associated with the procedure:
1. Rejection
- Acute Rejection: The body's immune system may attack the transplanted hand shortly after surgery. This requires immediate medical intervention.
- Chronic Rejection: Long-term rejection can occur, leading to the gradual loss of function in the transplanted hand.
2. Infection
- Surgical Site Infections: The risk of infection at the site of surgery, which can complicate recovery.
- Systemic Infections: Immunosuppressive medications, necessary to prevent rejection, increase the risk of infections throughout the body.
3. Complications from Immunosuppressive Therapy
- Side Effects: Medications can cause side effects such as weight gain, diabetes, high blood pressure, and kidney damage.
- Increased Cancer Risk: Long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs can increase the risk of certain cancers.
4. Functional Recovery Challenges
- Limited Functionality: Not all patients regain full functionality, and the extent of functional recovery can vary widely.
- Prolonged Rehabilitation: Intensive and prolonged rehabilitation is required, and full recovery can take years.
5. Psychological Impact
- Adjustment Issues: Some patients may struggle with the psychological aspects of adapting to a transplanted hand, including body image and identity issues.
- Emotional Stress: The stress of ongoing medical treatments and the uncertainty of outcomes can be significant.
6. Technical Complications
- Vascular Problems: Issues with blood flow to the transplanted hand can lead to tissue death and failure of the transplant.
- Nerve Regeneration: Nerve healing and regeneration are slow processes, and incomplete nerve recovery can limit hand function.
7. Cost and Accessibility
- High Cost: The procedure is expensive, including the surgery itself, immunosuppressive medications, and rehabilitation.
- Limited Availability: Access to skilled surgical teams and donor hands can be limited, making the procedure less accessible.
Conclusion
Hand transplant surgery carries significant risks and requires a careful weighing of potential benefits against these risks. Candidates for the surgery undergo extensive evaluation to determine if they are suitable for the procedure and to prepare them for the challenges ahead. Close monitoring, rigorous medical care, and dedicated rehabilitation are essential to maximizing the chances of a successful outcome.
preparation
How to Prepare for Hand Transplant Surgery?
Preparation for hand transplant surgery is a comprehensive and multidisciplinary process designed to ensure the best possible outcome. Here's a detailed overview of the steps involved:
1. Medical Evaluation
- Comprehensive Health Assessment: A thorough physical examination and review of medical history to assess overall health and suitability for surgery.
- Blood Tests: Blood typing and cross-matching to ensure compatibility with potential donors.
- Immunological Tests: Tests to assess immune status and potential for rejection.
2. Psychological Evaluation
- Mental Health Assessment: Evaluations by psychologists or psychiatrists to ensure the candidate is mentally prepared for the challenges of the surgery and the long-term commitment required.
- Support System: Assessment of the patient's support system, including family and friends, to ensure they have adequate emotional and practical support.
3. Pre-Surgical Counseling
- Education on Risks and Benefits: Detailed discussions about the potential risks, benefits, and outcomes of the surgery.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: Information on the need for lifelong immunosuppressive medication and its potential side effects.
4. Physical Preparation
- Nutritional Optimization: Ensuring the patient is in optimal nutritional health to promote healing and recovery.
- Physical Conditioning: Pre-surgical physical therapy to maintain or improve the strength and flexibility of the residual limb and overall fitness.
5. Organizing Logistics
- Coordination with Transplant Team: Regular communication with the transplant team to coordinate the timing and logistics of the surgery.
- Hospital Preparation: Admission to the hospital and preparation of the surgical suite.
6. Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Informed Consent: Obtaining informed consent after ensuring the patient understands all aspects of the surgery.
- Ethical Approval: Ensuring that the transplant procedure has been reviewed and approved by relevant ethical committees.
7. Pre-Surgical Tests and Procedures
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans of the residual limb to plan the surgical approach.
- Vascular Studies: Assessing the blood vessels to ensure they can support the transplanted hand.
8. Pre-Operative Instructions
- Fasting: Instructions on fasting before surgery, typically starting from midnight on the day of the surgery.
- Medication Management: Guidance on which medications to take or avoid before surgery.
9. Developing a Post-Operative Plan
- Rehabilitation Plan: Arranging for post-operative rehabilitation, including physical and occupational therapy.
- Follow-Up Schedule: Planning regular follow-up visits to monitor the progress of the transplant and adjust medications as needed.
10. Challenges and Considerations
- Donor Availability: Finding suitable donors remains a challenge due to the need for specific tissue matching.
- Cost: Hand Transplant Surgery Cost in India, covering surgery, post-operative care, and lifelong immunosuppressive therapy.
- Awareness and Accessibility: Increasing awareness about organ donation and improving accessibility to advanced medical facilities can enhance the success and reach of hand transplant surgeries in India.
- Best Hospitals : Searching the best Hand Transplant Surgery Hospital in India
Conclusion
Preparation for hand transplant surgery is a meticulous process that involves medical, psychological, and logistical planning. Ensuring that the patient is well-prepared physically, mentally, and emotionally is crucial for the success of the surgery and the subsequent recovery and rehabilitation. The involvement of a multidisciplinary team ensures that all aspects of the patient's health and well-being are addressed, increasing the chances of a positive outcome.
procedure
What is the procedures of Hand Transplant Surgery?
Hand transplant surgery is a complex and multidisciplinary procedure that involves multiple stages, from preoperative preparation to postoperative care. Here’s a detailed overview of the entire process:
Preoperative Preparation
- Medical and Psychological Evaluation:
- Comprehensive health assessment to determine overall suitability for surgery.
- Psychological evaluation to ensure mental preparedness for the procedure and the long-term commitment required.
- Donor Matching:
- Blood type and tissue compatibility testing.
- Identification and preparation of a suitable donor hand.
- Pre-Surgical Counseling:
- Discussions about the risks, benefits, and expected outcomes of the surgery.
- Information on the need for lifelong immunosuppressive therapy and its side effects.
- Physical Conditioning:
- Pre-surgical physical therapy to maintain or improve the strength and flexibility of the residual limb.
Surgical Procedure
- Anesthesia:
- General anesthesia is administered to the patient to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free during the procedure.
- Preparation of the Donor Hand:
- The donor hand is carefully harvested, preserving bones, tendons, blood vessels, nerves, and skin.
- The donor hand is kept in a cold, sterile solution to maintain its viability.
- Recipient Limb Preparation:
- The recipient’s residual limb is prepared for the transplant, including the removal of any non-viable tissue.
- Bone Fixation:
- The bones of the donor's hand are aligned and fixated to the recipient’s bones using plates and screws.
- Vascular Anastomosis:
- Blood vessels (arteries and veins) from the donor's hand are connected to those of the recipient using microsurgical techniques to restore blood flow.
- Nerve Repair:
- Major nerves are meticulously connected to allow for eventual sensation and motor function in the transplanted hand.
- Tendon and Muscle Attachment:
- Tendons and muscles are connected to enable movement and function of the hand.
- Skin Closure:
- The skin is carefully closed, and the hand is bandaged and immobilized to promote healing.
post procedure
Postoperative Care
- Intensive Monitoring:
- Close monitoring in the ICU for signs of rejection, infection, and complications.
- Regular blood tests and imaging studies to assess the health of the transplanted hand.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy:
- Lifelong administration of immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection of the transplanted hand.
- Monitoring and managing side effects of immunosuppressive drugs.
- Rehabilitation:
- Intensive physical and occupational therapy to regain function and strength in the transplanted hand.
- Gradual increase in the use of the hand as healing progresses.
- Follow-Up Care:
- Regular follow-up visits to monitor progress, adjust medications, and address any issues.
- Psychological support to help with the adjustment to the transplanted hand.
Potential Complications
- Rejection: Acute or chronic rejection of the transplanted hand.
- Infection: Increased risk of infections due to immunosuppressive therapy.
- Functional Recovery: Variability in the degree of functional recovery and possible limitations in hand function.
- Complications from Immunosuppressive Therapy: Side effects such as weight gain, diabetes, high blood pressure, and increased risk of certain cancers.
Conclusion
Hand transplant surgery is a highly specialized and intricate procedure that requires careful planning, a skilled surgical team, and comprehensive postoperative care. The goal is to restore function and improve the quality of life for individuals who have lost their hands due to injury or illness. With advances in surgical techniques and immunosuppressive therapy, the success rates of hand transplants continue to improve, offering hope to many patients.
success rate
What is the success rate for surgery of hand transplant surgery?
The success rate for hand transplant surgery, also known as vascularized composite allotransplantation (VCA), varies based on several factors, including the patient's overall health, the extent of the injury, and adherence to postoperative care protocols. Here are some key points regarding the success rates and outcomes:
Success Rates and Outcomes
- Survival of the Transplanted Hand
- High Survival Rates: The majority of transplanted hands survive if there are no major complications and if the patient adheres to the immunosuppressive regimen. The survival rate for the transplanted hand is generally high, with most hands surviving at least 1-5 years post-transplant.
- Functional Outcomes
- Functional Recovery: Many patients regain significant function in their transplanted hands, including the ability to perform daily tasks, although the degree of functional recovery can vary widely.
- Sensation and Motor Skills: Recovery of sensation and motor skills occurs gradually and can take several months to years. Some patients achieve near-normal function, while others may experience limited movement and sensation.
- Rejection Episodes
- Management of Rejection: Acute rejection episodes are common but can often be managed successfully with adjustments to immunosuppressive therapy. Chronic rejection remains a long-term concern.
- Preventive Measures: Strict adherence to immunosuppressive medications and regular follow-up care are crucial in preventing and managing rejection.
Reported Success Rates
- Initial Success
- Short-Term Success: Initial success rates, defined as the survival of the transplanted hand and immediate postoperative recovery, are high, typically above 85-90%.
- Long-Term Success
- Long-Term Functionality: Long-term success rates, which take into account the functionality and health of the transplanted hand, vary. Studies report that around 60-80% of patients experience good to excellent functional outcomes several years post-transplant.
- Quality of Life: Many patients report significant improvements in quality of life and psychological well-being after a successful hand transplant.
Factors Influencing Success Rates
- Patient Selection
- Ideal Candidates: Patients who are in good overall health, have a strong psychological profile, and are motivated to adhere to postoperative care protocols tend to have better outcomes.
- Surgical Expertise
- Experienced Teams: Success rates are higher in medical centers with experienced surgical teams and comprehensive transplant programs.
- Postoperative Care
- Adherence to Therapy: Strict adherence to immunosuppressive therapy and participation in rehabilitation programs are critical for long-term success.
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent follow-up visits and monitoring for signs of rejection and complications improve outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations
- Immunosuppressive Therapy
- Side Effects: Long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs can lead to significant side effects, including increased risk of infections and certain cancers.
- Rehabilitation
- Intensive and Long-Term: Extensive and prolonged rehabilitation is required to maximize functional recovery, which can be challenging for some patients.
Conclusion
The success rate for hand transplant surgery is generally favorable, with high initial success rates and promising long-term outcomes for many patients. The overall success depends on various factors, including patient selection, surgical expertise, adherence to immunosuppressive therapy, and comprehensive postoperative care. Despite the challenges, hand transplant surgery can significantly improve the quality of life and functional abilities of individuals who have lost their hands due to injury or illness.
faqs from doctor
FAQs for surgery of hand transplant surgery?
1. What is hand transplant surgery?
Hand transplant surgery, also known as vascularized composite allotransplantation (VCA), involves transplanting a hand or hands from a deceased donor to a recipient who has lost one or both hands. It requires the connection of bones, blood vessels, nerves, tendons, muscles, and skin.
2. Who is a candidate for hand transplant surgery?
Candidates typically include individuals who have lost one or both hands due to traumatic injury, infection, or medical conditions such as cancer. They must be in good overall health, mentally prepared, and committed to lifelong immunosuppressive therapy and extensive rehabilitation.
3. How are donors selected for hand transplant surgery?
Donor hands are selected based on blood type and tissue compatibility with the recipient. The donor hand must come from a deceased donor, and matching is crucial to minimize the risk of rejection.
4. What are the risks associated with hand transplant surgery?
- Rejection: Acute or chronic rejection of the transplanted hand.
- Infection: Increased risk due to immunosuppressive medications.
- Complications from Immunosuppressive Therapy: Side effects like weight gain, diabetes, high blood pressure, and increased cancer risk.
- Functional Recovery: Variability in the degree of regained function.
5. What is the success rate of hand transplant surgery?
Initial success rates, defined by the survival of the transplanted hand and immediate recovery, are high, typically above 85-90%. Long-term success rates, considering functionality and health of the hand, are around 60-80% several years post-transplant. And you need the Best Hand Transplant Surgeon in India for good results.
6. What does the surgical procedure involve?
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered.
- Donor Hand Preparation: The donor's hand is harvested and preserved.
- Recipient Limb Preparation: The residual limb is prepared.
- Bone Fixation: Bones are aligned and fixed.
- Vascular Anastomosis: Blood vessels are connected.
- Nerve Repair: Nerves are connected.
- Tendon and Muscle Attachment: Tendons and muscles are attached.
- Skin Closure: The skin is closed and the hand is bandaged.
7. What is the recovery process like after hand transplant surgery?
Recovery involves intensive monitoring for signs of rejection and complications, lifelong immunosuppressive therapy, and extensive physical and occupational therapy to regain function and strength. Regular follow-up visits are necessary to monitor progress and adjust medications.
8. How long is the rehabilitation process?
Rehabilitation is a long-term commitment and can take several months to years. It involves regular physical and occupational therapy to improve the function, strength, and dexterity of the transplanted hand.
9. What are the potential complications of immunosuppressive therapy?
- Infections: Increased susceptibility to infections.
- Side Effects: Weight gain, diabetes, high blood pressure, and increased risk of certain cancers.
- Organ Damage: Potential damage to organs like the kidneys and liver over long-term use.
10. How can patients improve the chances of a successful hand transplant?
- Adherence to Therapy: Strict adherence to immunosuppressive medication regimens.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Frequent visits to the transplant team for monitoring and adjustments.
- Rehabilitation Commitment: Active participation in rehabilitation programs.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support overall well-being.
11. Can a transplanted hand perform normal functions?
Many patients regain significant function, including the ability to perform daily tasks. However, the extent of functional recovery varies, and some may experience limitations in movement and sensation.
12. What is the long-term outlook for patients with a hand transplant?
With proper medical care, adherence to immunosuppressive therapy, and ongoing rehabilitation, many patients experience improved quality of life and functional abilities. Long-term success requires a lifelong commitment to health management.
13. How much cost will come for hand transplant Surgery in India?
The cost of hand transplant surgery in India can vary widely based on several factors, including the medical facility, the complexity of the surgery, the length of the hospital stay, postoperative care, and the need for lifelong immunosuppressive therapy. Here is a breakdown of the potential costs involved:
While it is difficult to provide an exact figure, here are some estimated costs based on typical expenses:
- Initial Surgery and Hospitalization
- Surgery and Immediate Hospitalization: ?20,00,000 to ?40,00,000 (approximately $25,000 to $50,000)
- ICU Stay: Additional costs depending on the duration of stay and level of care required
- Immunosuppressive Medications
- Monthly Costs: ?10,000 to ?50,000 (approximately $125 to $625) per month for lifelong immunosuppressive therapy
- Rehabilitation
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: ?50,000 to ?2,00,000 (approximately $625 to $2,500)
Conclusion
Hand transplant surgery offers a potential solution for individuals who have lost their hands, providing the possibility of restoring function and improving quality of life. However, it requires careful candidate selection, meticulous surgical technique, comprehensive postoperative care, and a strong commitment from the patient to adhere to treatment protocols.




















