What is the best treatment for autism

WHAT IS THE BEST TREATMENT FOR AUTISM?
Are we looking for the best treatment for autism at an affordable cost? Here, we answer the question and explain how to choose the top doctors for better results.
WHAT IS AUTISM?
Autism, or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects how a person thinks, communicates, interacts with others, and experiences the world. It is called a "spectrum" disorder because it includes a wide range of characteristics, abilities, and challenges that vary from person to person.
Key Characteristics of Autism:
-
Social Communication Differences
- Difficulty understanding social cues, body language, or facial expressions
- Challenges in forming and maintaining relationships
- Preference for direct, clear communication
-
Repetitive Behaviors & Special Interests
- Engaging in repetitive movements or speech (e.g., hand-flapping, echolalia)
- Intense focus on specific interests (e.g., trains, numbers, or a hobby)
-
Sensory Sensitivities
- Hypersensitivity (strong reactions to sounds, lights, textures, or smells)
- Hyposensitivity (reduced sensitivity to pain, temperature, or touch)
-
Unique Thinking & Learning Styles
- Strong attention to detail
- Preference for routines and predictability
- Strengths in specific areas like memory, logic, or creativity,
WHAT IS THE BEST TREATMENT FOR AUTISM?
There is no "cure" for autism, but there are many effective supports and therapies that help autistic individuals thrive. The best approach depends on the person's unique needs, strengths, and challenges. Here are some of the most effective treatments:
1. Behavioral & Developmental Therapies
✅ Speech Therapy – Helps with communication skills, including verbal and non-verbal communication.
✅ Occupational Therapy (OT) – Improves daily living skills like dressing, eating, and handwriting.
✅ Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) – Focuses on teaching new skills and reducing behaviors that may be harmful or disruptive.
✅ Social Skills Training – Helps with understanding social cues, making friends, and interacting with others.
2. Educational Supports
✅ Individualized Education Plan (IEP) – Custom learning plans for autistic students in schools.
✅ Special Education Services – Adjustments in teaching methods to match learning styles.
3. Sensory & Emotional Support
✅ Sensory Integration Therapy – Helps with sensory sensitivities (e.g., noise, lights, textures).
✅ Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Helps with managing anxiety, emotions, and social challenges.
4. Medical & Alternative Approaches
✅ Medication (if needed) – Some autistic people take medications to manage anxiety, ADHD, or sleep issues.
✅ Dietary & Lifestyle Changes – Some individuals benefit from a balanced diet, exercise, and structured routines.
5. Family & Community Support
✅ Parent Training & Support Groups – Helps parents and caregivers understand and support their autistic loved ones.
✅ Self-Advocacy & Autism Acceptance – Encouraging autistic individuals to embrace their identity and strengths.
What’s the Best Approach?
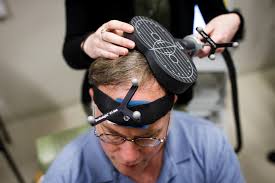
WHAT IS THE BENEFITS OF BRAIN STIMULATION THERAPY FOR AUTISM?
Potential Benefits of Brain Stimulation Therapy for Autism:
✅ Improved Social Skills – Some studies suggest TMS may help improve social awareness and communication.
✅ Reduced Repetitive Behaviors – Certain types of brain stimulation have been linked to a decrease in repetitive movements or behaviors.
✅ Better Emotional Regulation – May help with mood control, anxiety, and emotional responses.
✅ Enhanced Cognitive Function – Some evidence suggests mild improvements in attention, learning, and flexibility in thinking.
Types of Brain Stimulation for Autism:
🔹 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) – Uses magnetic pulses to stimulate specific areas of the brain, often tested for social and emotional regulation.
🔹 Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) – Delivers a low electrical current to the brain, sometimes used to improve cognitive function.
🔹 Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) – A more invasive procedure used in severe neurological conditions (rarely used for autism).
Is Brain Stimulation Therapy Safe?
Most non-invasive methods like TMS and tDCS are considered safe with minimal side effects, but they are still experimental for autism. Potential side effects may include:
⚠️ Mild headaches or discomfort
⚠️ Temporary changes in mood or emotions
⚠️ Unknown long-term effects (since research is still ongoing)
Should You Consider Brain Stimulation for Autism?
Right now, brain stimulation is not a first-line treatment for autism. Most experts recommend behavioral therapies, speech therapy, and sensory support as primary treatments. However, brain stimulation may be an option for individuals who have severe symptoms, anxiety, or depression that don’t respond to other treatments.
There’s no one-size-fits-all treatment for autism. The best support depends on the individual’s needs, interests, and goals. Early intervention is helpful, but people of all ages can benefit from accommodations and understanding.
Stem Cell Therapy for Autism: What You Need to Know
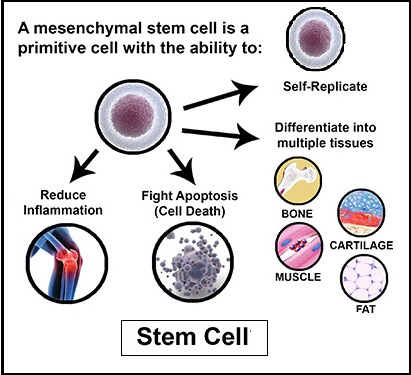
Stem cell therapy is an experimental treatment being studied for autism. Some researchers believe that stem cells might help repair brain inflammation and improve neurological function, but there is no proven cure for autism using stem cells yet.
1. How Might Stem Cell Therapy Work for Autism?
Stem cells have the potential to:
✅ Reduce Brain Inflammation – Some autistic individuals have higher levels of neuroinflammation, and stem cells might help reduce it.
✅ Improve Brain Connectivity – Stem cells might help repair or enhance neural pathways.
✅ Support the Immune System – Some studies suggest that immune dysfunction may play a role in autism, and stem cells could help regulate immune responses.
2. Types of Stem Cells Used in Autism Research
🔹 Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) – Derived from umbilical cord tissue, bone marrow, or fat.
🔹 Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) – Found in blood or bone marrow.
🔹 Neural Stem Cells – Can develop into different types of brain cells.
3. What Does the Research Say?
- Some small clinical trials suggest mild improvements in language, behavior, and social skills after stem cell therapy.
- However, the evidence is still limited, and results vary.
- No major health organizations (like the FDA or WHO) have approved stem cell therapy for autism yet.
HOW CAN I MANAGE THE AUTISM?
Managing autism is about understanding your strengths, challenges, and needs while creating a lifestyle that works best for you. Here are some strategies that may help:
1. Understanding Yourself
✅ Learn About Autism – Understanding how your brain works can help you find strategies that suit you.
✅ Identify Your Strengths & Challenges – Focus on what you're good at and find ways to work around difficulties.
2. Managing Sensory Sensitivities
✅ Create a Sensory-Friendly Environment – Use noise-canceling headphones, sunglasses, or weighted blankets if needed.
✅ Use Fidget Tools or Sensory Aids – Helps with focus and self-regulation.
✅ Take Sensory Breaks – Step away from overwhelming situations when needed.
3. Improving Social & Communication Skills
✅ Set Clear Social Boundaries – Learn to recognize and communicate personal space and needs.
✅ Use Scripts & Social Stories – Pre-plan conversations or responses for different situations.
✅ Join Autism Support Groups – Connect with others who understand your experiences.
4. Managing Routines & Daily Life
✅ Use a Planner or Apps – Helps with organizing daily tasks and reducing stress.
✅ Stick to Routines – Predictability can make life easier.
✅ Prepare for Changes in Advance – Use visual schedules or reminders to handle transitions smoothly.
5. Emotional & Mental Well-being
✅ Practice Self-Care – Engage in activities that relax and recharge you.
✅ Try Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Can help with managing emotions and anxiety.
✅ Use Mindfulness or Relaxation Techniques – Deep breathing, meditation, or exercise can help reduce stress.
6. Seeking Support When Needed
✅ Therapy & Coaching – Speech, occupational, or behavioral therapy may help.
✅ Self-Advocacy – Learn to express your needs in school, work, or daily life.
✅ Find a Supportive Community – Online forums, local groups, or autism organizations can offer guidance.
7. Career & Education Support
✅ Request Accommodations at Work or School – Adjustments like flexible schedules, quiet workspaces, or clear instructions can help.
✅ Focus on Strength-Based Careers – Jobs that align with your interests and strengths can be fulfilling.
Remember:
Autism isn’t something to "fix"—it's a different way of experiencing the world. Managing it means finding what works for you and embracing your unique strengths.
WHAT IS THE BEST MEDICINE FOR AUTISM?
There is no single "best" medicine for autism because autism itself is not an illness but a neurological difference. However, some medications can help manage specific challenges that some autistic people experience, such as anxiety, hyperactivity, depression, or sleep difficulties.
1. Medications for Common Autism-Related Challenges:
🔹 Anxiety & Depression
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) (e.g., Fluoxetine, Sertraline)
✅ Helps with anxiety, mood swings, and obsessive behaviors.
⚠️ Side effects: Nausea, drowsiness, or changes in appetite.
🔹 Hyperactivity, Impulsivity & ADHD Symptoms
- Stimulants (e.g., Methylphenidate [Ritalin], Amphetamines [Adderall])
✅ Helps with focus, attention, and reducing impulsivity.
⚠️ Side effects: Sleep issues, decreased appetite, irritability. - Non-Stimulants (e.g., Guanfacine, Clonidine)
✅ Helps with hyperactivity and emotional regulation.
🔹 Irritability & Aggressive Behavior
- Atypical Antipsychotics (e.g., Risperidone, Aripiprazole)
✅ FDA-approved for reducing severe aggression, self-injury, and irritability.
⚠️ Side effects: Weight gain, drowsiness, hormonal changes.
🔹 Sleep Problems
- Melatonin
✅ A natural supplement that helps with sleep cycles.
⚠️ Usually safe with few side effects.
2. Important Considerations
⚠️ Not everyone with autism needs medication. It depends on specific challenges.
⚠️ Medication should always be prescribed by a doctor after evaluating the individual's needs.
⚠️ Behavioral and therapy-based supports (like speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training) are often the first line of treatment before medication is considered.