Stem cell therapy for autism in india
STEM CELL THERAPY FOR AUTISM IN INDIA
Are you looking for Stem cell Therapy For Autism in India at an affordable cost, in a well-known center? Please contact us on WhatsApp / Viber/ Telegram +91 9582708782
Autism, or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a developmental condition that affects how a person perceives, communicates, and interacts with others. It is called a "spectrum" disorder because it encompasses a wide range of characteristics, abilities, and challenges. People with autism can have very diverse experiences, ranging from mild to severe.
Key Features of Autism:
- Social Interaction Challenges:
- Difficulty understanding social cues, such as facial expressions or tone of voice.
- Challenges forming and maintaining relationships.
- Preference for being alone or interacting in specific ways.
- Communication Differences:
- Delayed speech or language development.
- Nonverbal communication methods, such as gestures or facial expressions.
- Difficulty understanding metaphors, sarcasm, or abstract language.
- Repetitive Behaviors and Routines:
- Repeated movements or phrases (e.g., hand-flapping, echolalia).
- Strong preference for routines and resistance to change.
- Intense focus on specific interests or topics.
- Sensory Sensitivities:
- Over- or under-sensitivity to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, textures, or smells.
- Difficulty in noisy or crowded environments.
Causes of Autism:
The exact cause of autism is not fully understood, but research suggests it results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is not caused by vaccines, as extensive studies have debunked this myth.
Diagnosis and Support:
- Autism is typically diagnosed by developmental specialists, psychologists, or pediatricians based on observed behaviors and developmental history.
- Early intervention, therapies (like speech, occupational, or behavioral therapy), and support can help individuals develop skills and navigate challenges.
- Many autistic individuals have unique strengths, such as attention to detail, strong memory, or deep knowledge of specific interests.
Strengths and Diversity:
Autism is not inherently a disability but a different way of experiencing the world. Many people with autism, often referred to as "neurodivergent," contribute significantly to society and enrich our understanding of human diversity.
STEM CELL THERAPY FOR AUTISM
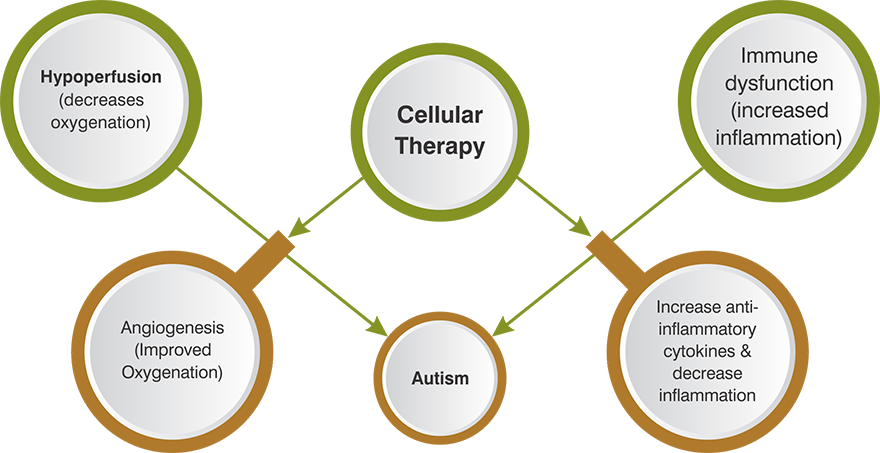
Stem cell therapy is an emerging area of research in the treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). The idea behind using stem cells is based on their ability to repair and regenerate tissues, reduce inflammation, and potentially restore normal brain function by modulating the immune system. While it has garnered interest, it is important to approach this topic with caution, as the therapy is still experimental and not yet widely approved.
How Stem Cell Therapy May Work for Autism
Researchers hypothesize that stem cells could help in the following ways:
- Reducing Inflammation: Many studies suggest that neuroinflammation may play a role in autism. Stem cells may reduce inflammation in the brain and improve communication between neurons.
- Modulating the Immune System: Abnormal immune responses are observed in some individuals with autism. Stem cells might help regulate immune responses, creating a more balanced environment in the body.
- Promoting Neural Connectivity: Stem cells have the potential to repair damaged or underdeveloped neural networks, possibly improving cognitive and behavioral functions.
Types of Stem Cells Studied for Autism
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Found in bone marrow, fat tissue, and umbilical cords, MSCs have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties.
- Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells: These stem cells contain a mix of progenitor cells and growth factors that may promote neuroregeneration.
- Neural Stem Cells: These are specific to the nervous system and may help in repairing neural pathways.
Current Research and Evidence
- Promising Results: Early-phase clinical trials and case reports suggest some improvement in behavioral and communication skills in individuals treated with stem cell therapy. However, these results are not consistent across all studies.
- Lack of Conclusive Evidence: Large-scale, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies are still lacking. Without robust evidence, it is difficult to determine the true efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy for autism.
Safety Concerns and Risks
- Unknown Long-Term Effects: The long-term safety and efficacy of stem cell treatments are not yet well understood.
- Risk of Complications: These may include infection, immune reactions, or unintended effects such as tumor growth.
- Unregulated Treatments: Many clinics worldwide offer unproven and unregulated stem cell therapies, often at high costs, with no guarantee of safety or effectiveness.
Current Recommendations
- Consult Experts: Speak with a qualified healthcare provider or autism specialist before considering any experimental treatments.
- Focus on Evidence-Based Therapies: Behavioral therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and other well-researched approaches remain the standard treatments for autism.
- Participate in Clinical Trials: If interested in stem cell therapy, consider enrolling in reputable clinical trials to ensure safety and contribute to scientific research.
WHAT'S THE PROCEDURES IN STEM CELL THERAPY FOR AUTISM?
The procedures for stem cell therapy in autism vary depending on the type of stem cells used, the clinic or medical facility, and the specific protocols of the treatment program. However, the general process involves several key steps:
1. Initial Consultation and Assessment
- Evaluation: The patient undergoes a thorough medical evaluation, including a review of medical history, current health status, and autism symptoms.
- Diagnostic Tests: These may include blood tests, imaging studies, and behavioral assessments to ensure the patient is a suitable candidate for stem cell therapy.
2. Stem Cell Collection
The source of stem cells determines how they are obtained:
- Umbilical Cord Blood: Stem cells are derived from donated umbilical cord blood, often collected at childbirth and stored in cord blood banks.
- Bone Marrow Aspiration: In some cases, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are extracted from the patient’s bone marrow, typically taken from the hip bone under local or general anesthesia.
- Adipose Tissue (Fat): MSCs can also be extracted from fat tissue, collected through a minimally invasive liposuction procedure.
- Pre-donated Cells: Some clinics use pre-stored or donor stem cells, which undergo rigorous testing to ensure safety and compatibility.
3. Stem Cell Preparation
- Processing: The collected stem cells are processed in a laboratory to isolate and prepare them for therapeutic use. This involves cleaning, enriching, and sometimes expanding the number of cells.
- Quality Control: The cells are tested for sterility, viability, and function before being used in treatment.
4. Stem Cell Administration
The method of administration depends on the treatment plan:
- Intravenous (IV) Infusion: Stem cells are delivered directly into the bloodstream via a vein. This is the most common method for autism treatment.
- Intrathecal Injection: Stem cells are injected into the cerebrospinal fluid through a lumbar puncture to target the central nervous system more directly.
- Intranasal Delivery: In some cases, stem cells are administered through the nasal passage to bypass the blood-brain barrier and reach the brain.
The procedure is usually performed under sterile conditions, and patients may be under sedation or anesthesia, depending on the method.
5. Post-Treatment Monitoring
- Observation: After the procedure, the patient is monitored for any immediate side effects, such as allergic reactions or infection.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to assess progress, track changes in behavior or symptoms, and address any concerns.
- Therapies and Support: Stem cell therapy is often combined with behavioral, speech, or occupational therapies to maximize potential benefits.
6. Ongoing Care
- Tracking Improvements: Families and clinicians document changes in communication, behavior, and social interaction over time.
- Adjustments: Based on the patient’s response, additional treatments or supportive therapies may be recommended.
Estimated Timeline
- Preparation Phase: 1–2 weeks (consultations, tests, and stem cell preparation).
- Treatment Phase: 1–3 days (cell administration and immediate monitoring).
- Post-Treatment Monitoring: Ongoing over months, often including periodic assessments.
Important Notes
- Individualized Treatment: Each patient’s treatment plan is personalized based on their unique needs and medical condition.
- Experimental Nature: Stem cell therapy for autism is not yet a standard treatment and is considered experimental.
- Safety Precautions: Ensure that the clinic or facility is reputable, follows ethical guidelines, and adheres to strict safety protocols.
HOW MUCH STEM CELLS USED IN AUTISM?
The number of stem cells required for autism therapy depends on various factors, including the individual's age, weight, severity of autism symptoms, and the specific treatment protocol being followed. Since stem cell therapy for autism is still experimental, there are no universally established guidelines for the number of cells needed. However, clinics and research studies generally provide a range based on their experience and protocols.
Common Dosages in Research and Treatment
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs):
- Typical doses range from 1–2 million cells per kilogram (kg) of body weight.
- For a child weighing 20 kg (44 lbs), the dose might be 20–40 million MSCs.
- Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells:
- Dosages vary but may involve 50–200 million cells per infusion.
- The exact number depends on the quality and type of cord blood used.
- Neural Stem Cells:
- These are typically administered in smaller quantities, and the dosage is determined by the protocol of the specific research or clinic.
- Multiple Sessions:
- Some protocols involve multiple treatments spread over weeks or months, with each session using a certain number of cells.
- For example, a clinic might administer 20–40 million cells per session over 2–4 sessions.
Factors Affecting Dosage
- Child vs. Adult: Children generally require fewer stem cells than adults due to their smaller size.
- Type of Stem Cells: Different stem cell types (e.g., MSCs, umbilical cord-derived, adipose-derived) have varying potency and therapeutic effects.
- Administration Method: The delivery method (intravenous, intrathecal, or intranasal) can influence the dosage needed.
Experimental Nature and Safety
Because stem cell therapy for autism is still in the research phase:
- Dosages are determined based on clinical trial protocols and are subject to ongoing study.
- Excessive or inappropriate dosages could pose risks, such as immune reactions or other side effects.
- Treatments should only be conducted under the supervision of qualified professionals in regulated settings.
STEM CELL THERAPY COST FOR AUTISM IN INDIA
Stem cell therapy for autism Cost in India is an emerging treatment varying based on factors such as the medical facility, location, type of stem cells used, and the specific treatment protocol. Generally, the cost ranges from approximately 8000 to 12000 USD per treatment cycle.
Cost Breakdown
- Lower Range: Some sources indicate that stem cell therapy for autism starts around $5,000 to $8,000 (approximately ₹3,65,000 to ₹5,84,000).
- Average Cost: Other estimates suggest an average cost starting from $12,000 (about ₹8,76,000).
- Higher Range: In certain cases, costs can escalate up to $50,000 (approximately ₹36,50,000), depending on the complexity and specifics of the treatment.
Factors Influencing Cost
- Type of Stem Cells: The source and processing of stem cells (e.g., autologous vs. allogeneic) can impact the overall cost.
- Number of Treatment Cycles: Multiple sessions may be required, affecting the total expenditure.
- Hospital Facilities and Location: Premium medical centers in metropolitan areas may charge higher fees compared to those in other regions.
Considerations
- Lack of Standardization: Stem cell therapy in India for autism is still experimental, and there is no standardized treatment protocol, leading to significant cost variations.
- Insurance Coverage: As of October 2020, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) includes modern treatments like stem cell therapy under standard health insurance plans. However, coverage specifics can vary, so it's advisable to consult with your insurance provider.
- Efficacy and Safety: It's crucial to note that the effectiveness of stem cell therapy for autism is not conclusively proven, and the treatment is not universally recommended in clinical practice. Some reports indicate that families have incurred significant expenses, ranging from ₹5,00,000 to ₹10,00,000, without achieving the desired outcomes.
Recommendations
Before considering stem cell therapy for autism:
- Consult Healthcare Professionals: Seek advice from qualified medical experts to understand the potential benefits and risks associated with the treatment.
- Verify Clinic Credentials: Ensure that the medical facility is reputable and complies with national medical guidelines.
- Consider Alternative Therapies: Explore established and evidence-based treatments for autism, such as behavioral therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy.
In summary, while stem cell therapy for autism in India is available with costs ranging from approximately 8000 to 12000 USD per treatment cycle, it's essential to approach this option with caution due to the lack of conclusive evidence regarding its efficacy and safety.
Final Thoughts
Stem cell therapy holds potential for treating autism, but it is still in the experimental phase. Until more rigorous studies validate its safety and efficacy, it should be approached cautiously. Families and individuals considering this option should thoroughly research and consult trusted medical professionals.